- Global Capability Centres are hubs created by firms that focus on analytics, operations, technology and innovation.
- Lack of GCCs leads to greater operating costs, disconnected efficiency, limited talent reach, and a significant reduction in business resilience.
- A Global Capability Center (GCC) ensures cost-effective processes, reinforces innovation, improves resilience, and makes workflows seamless.
Table of Contents
- What is a Global Capability Center?
- The Evolution of Global Capability Center
- Core functions performed by Global Capability Center
- Why Global Capability Center are the Go-To Solution for Enterprises
- Why Companies Are Setting up GCCs in India, Eastern Europe, Philippines, etc.
- Outsourcing vs GCC vs SSC: A Brief Comparison
- Why Companies Should Invest in Global Capability Center
- Operating models under GCC services
- The Future of Global Capability Centers
- Conclusion
Digital tools and technology are changing how global firms operate. Enterprises globally today depend on this digital transformation to serve current market trends and customers. The scale of this change is growing fast as companies increasingly rely on tech-enabled Global Capability Centers (GCCs) to execute daily tasks. GCCs are not just about cost arbitrage anymore — they have become a strategic backbone for many enterprises. They are now value creators as well as the innovation hubs responsible for operations, technology, and support.
70 % of Fortune 500 companies use GCCs for global innovation
Source: https://community.nasscom.in/This article discusses the purpose of GCCs, their benefits, the various operating models, and their future in the global market.
What is a Global Capability Center?
A GCC is a legal offshore entity or unit owned and run by the parent corporation. It is created to concentrate on advanced solutions including data, analytics, IT and process improvements. All this and more to improve the performance of the controlling firm.
Global Capability Centres have changed from normal cost capitals to high-impact hubs for digital innovation. They provide advantages such as complete operational authority and scalability, which makes GCC a successful model for business agility.
Based on research, GCCs are anticipated to enhance value for their parent companies at a CAGR of 11 -12% during FY25 – 29
Source: https://www.pwc.in/The Evolution of Global Capability Center
If you look at Global Capability Centres (GCCs) now compared to the ’90s, they’re like night and day. Back then, these centers were all about churning through paperwork, handling payroll and answering phones.
Fast forward to today, and GCCs aren’t just about cutting costs. They are all about pushing business growth, coming up with new ideas, and actually making a real difference, not just keeping the wheels turning. Let us understand the various phases of the evolution of GCCs over the past years.
Phase 1: Cost savings (1990 to 2005)
They started as centers that concentrated on costs to operate simple and transactional activities. The results were- improved efficiency and minimized expenses while focusing on support services including finance, IT support, and customer support.
Phase 2: Augmentation and diversity (2005 to 2015)
The Global Capability Center extended its horizon to perform skilled functions such as developing software, performing data analytics, and optimizing processes. This improved operational efficiency and increased cost savings.
Phase 3: Innovation and action (2015 to present)
After stages 1 and 2, the GCC entered its current stage, transforming into a key partner that drives innovation, digital capabilities, and rebuilds business systems.
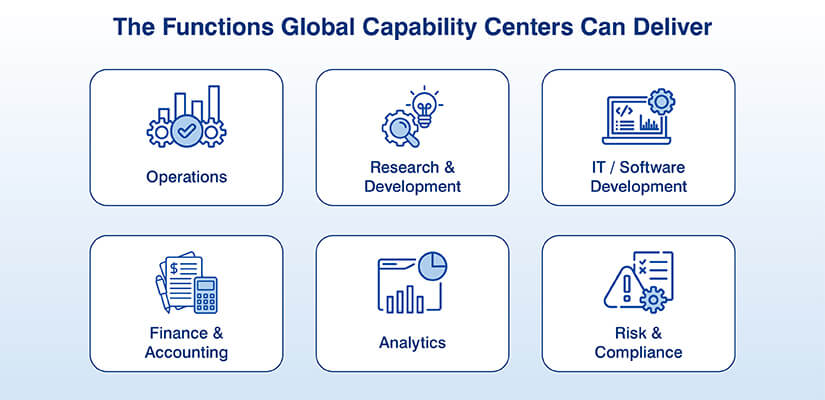
Core functions performed by Global Capability Center
GCCs excel in performing business functions such as Research and Development (R & D), analytics, and engineering design. For research and development, GCCs are driven by innovation to build new products, improve existing ones, and solve complex problems.
Within analytics, they use AI and machine learning to build insights, enhance processes, and support faster decision-making. For product design, GCCs usually manage comprehensive product engineering, along with software development and systems integration for the entire development lifecycle.
Why Global Capability Center are the Go-To Solution for Enterprises
GCCs enable firms from any country to set up their business offices through centralization or using a multi-location model. GCCs not only offer the required skill set, but also the latest digital tools needed to operate across multiple markets and time zones, helping companies reduce costs, accelerate delivery, and generate new ideas.
How GCCs Solve Enterprise Challenges
GCCs are able to manage fundamental operations based on new models that depend on tech, large talent pools, and unified systems. This increases efficiency and helps firms stay competitive in an evolving market.
Some GCCs are owned and managed by parent firms and are created to handle high-value operations across automation, analytics, and product engineering. This ensures that corporate goals are aligned and data is kept secure along with compliance by ensuring in-house control. These in-house entities may later convert into excellence centres to create new business models.
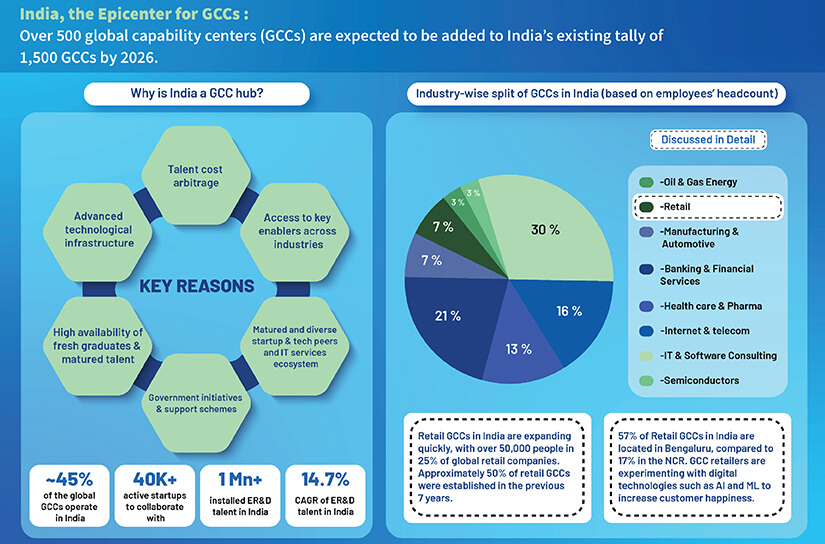
Why Companies Are Setting up GCCs in India, Eastern Europe, Philippines, etc.
Global Capability Centers are increasingly being set up in various locations, including India, Eastern Europe, and the Philippines for numerous advantages.
A country like India offers an expansive and skilled workforce within engineering and technology along with English proficiency and STEM individuals. Europe helps parent companies use advanced markets with an extensive industry expertise and regulatory framework that helps them stay in close proximity with their channel partner and clients. The Philippines draws global firms based on proficiency in English, cultural alignment, extensive talent pool, and cost motivation.
Outsourcing vs GCC vs SSC: A Brief Comparison
Here is a 5-point comparison of Outsourcing vs Global Capability Centers (GCC) vs Shared Services Centers (SSC). The table identifies the efficiencies of SSC and GCCs focus on driving innovation. Outsourcing is concentrated on execution and costs.
| Characteristic | Outsourcing | Global Capability Centers. | Shared Services Centers. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership and control. | Limited control managed by third-party systems. | Owned and controlled by the parent firm. | Internal ownership to centralize transactional activities. |
| Scope and Focus. | Transactional and cost-led. | Strategic and value-driven. | Regularized and repetitive. |
| Skills. | Driven by workforce of the vendor. | Backed by innovation and skill. | Centred on processes and efficiency. |
| Innovation. | Restricted to contract-driven services. | Encourages strategic abilities. | Concentrated toward process enhancement and cost trimming. |
| Information security. | Third-party involvements can cause higher risks. | Inspires compliance and quality control. | Services are controlled by regularized guidelines. |
Why Companies Should Invest in Global Capability Centers
Firms usually invest in GCCs as they provide various advantages that help innovation and high-value outcomes. They can expedite business growth through quick product development, refined workflows, and worldwide coordination. Using digital transformation tools such as AI and analytics, GCCs can cut operational costs by 40 – 60%. Beyond costs, they also offer compliance, flexibility, and security.
Top 4 benefits of Global Capability Centers

Cost efficiency with value creation
GCCs create value by reducing expenses on infrastructure, salary, and operations. They help firms reinvest in growth, competitiveness, and innovation for greater agility and advantages.
Operational cost savings.
Operational expenses are minimized by combining processes and removing duplication. Centralized management reduces overhead costs for utilities, office areas, and vendor contracts. Using automation and bespoke processes improves efficiency and prevents errors. Firms can realize 25% – 40% savings on operations costs within a small timeframe.
Skilled workforce at a lower cost.
GCCs can use an extensive talent pool from cost-effective locations where remunerations are lower by 30 – 60%. Hiring from tier-2 cities lowers expenses by more than 30%. Retaining the talent pipeline minimizes training expenses. This provides sustained commercial benefits without compromising quality.
Moving beyond “cheap labor” to “value-driven expertise.”
Tapping into a workforce that can create innovation and execute tasks like engineering, R & D, and analytics creates quick product development and decision-making. Well planned training and career enhancement optimizes employee performance and retention.
Innovation and digital transformation
GCCs act as hubs to achieve digital transformation for parent firms. Rapid use of new digital transformation tools optimize efficiency and client experience. Companies can be competitive by including agility and innovation.
Driving AI, ML, automation, and cloud initiatives.
Incorporating AI, ML, automation, and cloud-driven tools can automate processes and create actionable understanding. Cloud technologies can scale computing performance and team collaboration. These platforms prevent manual issues and speed up digital functions to create an impact.
Serving as global R&D and innovation hubs.
Acting as R & D hubs, GCCs can help companies create new products and refine existing ones. Using a large talent pool creates ideas that are new. These hubs can reduce development cycles and help with uninterrupted innovation. Global distribution aligns transformation with the market requirements.
Contribution to business transformation beyond back-office operations.
Setting up GCCs helps firms with end-to-end improvements. They redesign workflows, combine digital tools, and improve client engagement. Strategic goals are set in place to work on new models and generate revenue channels. If you are looking for continuous growth and a substantial edge, GCC works as a catalyst for that.
Global standardization and process control
Implementing well-planned processes improve consistency across various locations. Uniform process control ensures best practices and policies are adhered to. It eliminates errors and improves efficiency.
Consistency in processes and operations across geographies.
Utilizing centralized systems and protocols creates uniformity in services and the output across multiple locations. Consistency ensures brand trust, enhances customer satisfaction and streamlines collaboration.
GCCs as an extension of HQ, not just a vendor.
GCCs are important entities of the parent firm that are aligned with the corporate scope. Managed internally, they provide better control, greater collaboration, and integration of various cultures. They support innovation and strategic ambition by staying close to the controlling company.
Improved compliance, data security, and governance.
Robust data protocols set with global regulations and standards allow greater control over sensitive data and minimizes the risk of any violation. Frameworks for governance facilitate ethical, legal, and industry-led needs. This builds trust in stakeholders and regulatory groups.
Strategic value and competitive advantage using GCC as a service
GCCs create a high impact on a firm based on creation and operational distinction. It ensures quick decision-making and adaptation. They also help companies stay ahead by extending capabilities, agility, and long-term benefits.
Enhancing customer experience.
Using analytics and combining services helps GCCs provide precise and personalized experiences for customers. Processes become seamless for quick issue resolution and customer requirements are anticipated faster. Services improvements are done with uninterrupted feedback from clients. This ensures brand loyalty and greater satisfaction.
Supporting market expansion strategies.
By providing GCC services and products to local requirements ensures market expansion. It also helps companies with innovation scaling and testing in numerous areas. Firms can venture into new markets with local strategies and a quick time to market.
Operating models under GCC services
Global Capability Centers are run using various models that are customized to serve various business requirements and mitigate risks. These models vary in control, ownership, and operations between the parent enterprise and third parties. Selecting the appropriate model is important to align objectives of the GCC with strategic ideas of the company.
The primary GCC models are Captive, Build-Operate-Transfer, and Joint Venture that provide collaboration and control at various levels. Each model delivers unique benefits, scalability, and operational control to enhance value.
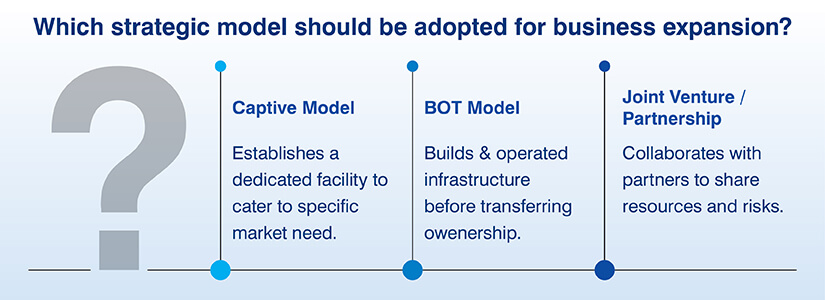
Captive Model:
The Captive model is owned and operated by the umbrella organization. It provides complete control over talent acquisition, jurisdiction, and processes. The following model ensures goals fall in line with bigger strategies of the organization. It ensures security of intellectual property and important data, which makes it suitable for firms with multiple proprietary functions. Using this model requires a significant investment and stretched setup timelines, but delivers greater cost efficiencies.
Example: Microsoft Development Center (India)
The Global Capability Center for Microsoft situated at 2 locations : Hyderabad and Bengaluru is a captive model which is owned and operated by Microsoft. It plays an important role in product engineering, software development, and innovations in Office Suite, Windows, and the Azure Cloud. The center uses a talent pool from India to enable technology transformations such as AI and ML. It helps Microsoft keep control over the patent and product quality.
BOT (Build-Operate-Transfer) Model:
This model provides a phased alternative as third-party vendors create the initial setup and operate the GCC on behalf of the parent company. During this timeframe, the vendors setup the infrastructure, on board processes, and facilitate operational management. This step minimizes the initial investment for the principal company and reduces risks. After a suitable time, ownership and management are given to the original firm. This model is suitable for companies who seek new industries or locations led by flexibility.
Example: IMEG(USA) with HitechDigital
IMEG is a design and engineering firm in the US that provides building systems, infrastructure, and construction-driven services. They partnered with HitechDigital to expand their volume, lower cycle times, and improve operational costs.
Both the teams work on a Build, Operate, and Transfer model. HitechDigital with its expertise helped IMEG set up two delivery centers- one in Bengaluru and the other at Vizag. While the delivery centers are based in India, IMEG provides the operations team and HitechDigital is in charge of the team management.
The collaboration between IMEG and HitechDigital opened doors to opportunities that led to:
- Cost and resource optimization
- Reduction in TAT with collaboration
- Quick capability scaling
- On boarding new firms through resource mergers
Joint Venture / Partnership:
In a JV, the core company collaborates with external parties to own and manage the GCC through a partnership. The investment and risks are divided that enables access to expertise, infrastructure, and knowledge. It integrates the capabilities of both the entities that leads to quick market entry and scalability. GCCs built on partnerships offer higher flexibility while building a major impact on strategic operations.
Example: HSBC in collaboration with Tech Partner.
HSBC is a leading bank that has set up GCCs in multiple regions of India using JVs from local providers and technology vendors. In a partnership, HSBC benefits from local knowledge and tech expertise of partners. This speeds up market magnification and helps HSBC divide the involved risks and responsibilities while making sure it is in line with the strategies of the parent firm.
The Future of Global Capability Centers
GCCs are innovation hubs led by AI. They focus on flexibility, digital frameworks, and sustainability. They will guide decisions in the boardroom and plans on a global setting.
Rise of AI-driven GCCs with automation-first approaches
Automation along with AI is making GCC operations better by simplifying workflows and eliminating human flaws. These tools ensure customer interactions that are customized, allow predictive analysis, and quick execution. Automation helps firms focus on core business tasks, while AI creates quick results.
Tier-2/Tier-3 city expansion for better costs and access to untapped talent
Taking GCCs into Tier 2 and 3 cities provides greater access to talent resources with exceptional technical expertise. These locations significantly reduce infrastructure and labor costs in comparison to metro regions. The support of local government bodies provides incentives and minimizes reliance on urban areas, and reduces business risks. Operations are diversified to maintain quality and cost effectiveness.
Sustainability and ESG integration in GCC operations
GCCs are integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards into business culture and operations. Using these principles lowers the carbon footprint through digital transformation workflows and efficient infrastructure. Social initiatives for hiring, employee welfare, and community engagement are combined with governance practices that ensure ethics, compliance, and transparency.
Conclusion
Back offices are increasingly being converted into strategic growth drivers with Global Capability Centres. As they continue to breathe agility and change into global firms, they also improve cost efficiency, access to talent, and expedited innovation.
Looking into the future, GCCs will be reinforced with AI-led tools and innovative strategies to create global recognition. Extending to Tier 2 and 3 cities enhances cost effectiveness and talent diversity, while incorporating ESG and sustainability enriches corporate responsibility and long-term business value.




