- Quality control in sheet metal fabrication design drafting is a comprehensive process that spans from design conceptualization to detailing, ensuring functional integrity and fabrication efficiency.
- Implementing a standardized quality control process is critical for CAD teams to achieve efficiency and consistency in sheet metal drawings, thereby maintaining high-quality standards.
- Leveraging technology and adhering to a robust quality control framework ensures quality without escalating costs and optimizes the CAD detailing process for metal fabrication shops.
Table of Contents
- What is Sheet Metal Detailing
- Why Quality Control Matters in Sheet Metal Detailing
- Importance of a Standardized Process for Consistency and Efficiency
- Common Quality Control Challenges in Sheet Metal Fabrication
- How To Build a Quality Control Plan for Sheet Metal Detailing
- Top Techniques For Quality Control In Sheet Metal Design
- Technology-Driven Approaches to Sheet Metal Drafting Quality Control
- Compliance with Industry Standards and Certifications
- How Expert Sheet Metal CAD Drafting Teams Solve QC Challenges
- Future Trends and Innovations in Quality Control
In the sheet metal industry, quality control and validation are key measures that protect the fabricator from the risks of losses caused by low-quality detailing, and rework.
A strong quality control framework facilitates the effective transition from sheet metal design detailing to manufacturing. Precise quality standards, process mapping for improved oversight, and strict inspection protocols are key elements of this standardized approach that promotes production consistency and efficiency. These steps ensure that detailing goes beyond specifications to promote reliability in each bend and fold.
Quality control is not simply a final review. It’s a methodical process of checks for dimensional accuracy, material integrity, and product craftsmanship spanning from design to delivery, and ensuring products meet or exceed set standards. For the sheet metal fabricator, diligent quality control and validation steps lay down the path to success.
What is Sheet Metal Detailing
Sheet metal detailing is the process of creating detail drawings and specifications for the fabrication of sheet metal. It produces 2D or 3D shop drawings from architectural or engineering drawings that show the dimensions, tolerances, materials, and bend allowance associated with the fabrication of a component. These drawings serve as a guide for manufacturers to ensure components are manufactured correctly, and that they fit together.
This is a vital process in many industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial equipment manufacturing. Valid sheet metal detailing lowers mistakes, reduce material waste, and costly rework. It is especially vital for complex parts requiring close tolerances or multiple bends, to ensure efficient and consistent production. A quality control and validation process are often used to determine standards within the industry for ensuring the drawings are valid prior to starting fabrication.
In modern practices sheet metal detailers frequently utilize CAD/CAM software, automated validation, and collaborative features. When used in conjunction with rigorous quality control, they may allow the fabricators to produce quality products in large quantities that are all accurate, more efficient, and consistent.
Why Quality Control Matters in Sheet Metal Detailing
Quality control (QC) plays a significant role in assuring that sheet metal components are manufactured with precision and reliability. Identifying errors from the detailing scope of work for incorrect dimensions, missing tolerances, or improper material interpretations can result in costly rework, delays in product delivery, and increased material waste, as well as poor-detailing errors that impact other subsequent processes including welding, bending, and assembly, and both timeline and project costs.
Conversely, proper QC in sheet metal detailing provides measurable benefits. The fabrication drawings are accurately and consistently produced with compliance to existing standards in the industry. Quality assurance validates designs and ensures components are made in accordance with the design; it even provides waste reduction and improves production efficiency on the fabrication floor. However, the most beneficial component of QC is client trust to guarantee the project will be delivered on time, within budget, and with the specified quality.
Manufacturing today with competition across the globe, especially in the sheet metal industry, means that QC for specific processes or procedures is now a part of the first step; it is not just an added process but has become a requirement for processes to remain efficient, responsible to risks involving projects, and most importantly, to maintain the business in the long term.
Importance of a Standardized Process for Consistency and Efficiency
A standardized quality control process is the backbone of efficiency and consistency in sheet metal fabrication. It creates a predictable and repeatable workflow, which is essential for efficient resource allocation and scheduling.
Moreover, a standardized process streamlines operations, reducing the time and cost associated with ad-hoc quality checks or unplanned reworks. It ensures that every product meets the same high standards. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining client trust and brand reputation.
Common Quality Control Challenges in Sheet Metal Fabrication
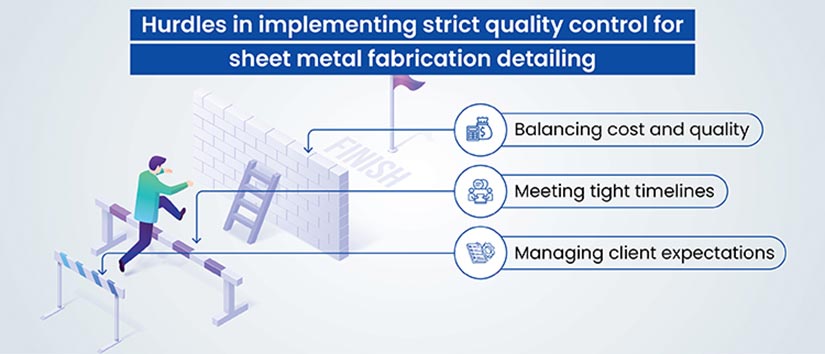
Quality control in sheet metal fabrication detailing entails several challenges that can significantly impact the final product’s integrity and client satisfaction. Here are key challenges and their implications:
- Balancing Cost and Quality: Achieving the right balance between cost and quality is crucial. High-quality standards often increase costs, while cost-cutting can compromise quality. Companies need to innovate and optimize to maintain quality without escalating costs, such as through efficient material use and leveraging technology.
- Meeting Delivery Timelines: Maintaining quality within strict delivery schedules is challenging. Delays in any fabrication stage can affect overall timelines. Efficient project management and streamlined processes are essential to ensure timely delivery without compromising quality.
- Managing Client Expectations with Quality Deliverables: Aligning fabrication processes with unique client expectations, while upholding quality standards, is a significant challenge. This requires understanding client needs, clear communication, and process adaptability to deliver customized, high-quality solutions.
The key to overcoming these challenges is partnering with an expert CAD drafting team specializing for the sheet metal fabrication industry. Strategic planning, innovative approaches, and effective communication help enhance quality, bring down costs, and increase client satisfaction.
How to Build a Quality Control Plan for Sheet Metal Detailing
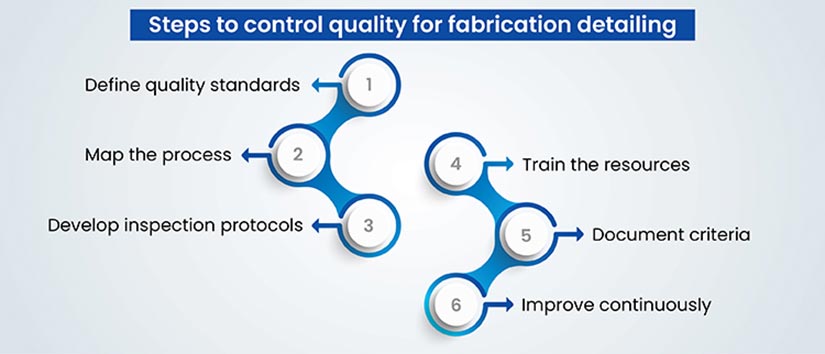
- Define Quality Standards: The first step is to establish clear, measurable quality standards based on industry norms, client requirements, and regulatory guidelines. These standards should cover all aspects of the fabrication process, including material selection, design tolerances, and finishing.
- Process Mapping: Outline each step of the fabrication process. This helps in identifying critical control points – stages where inspections or tests are essential to ensure quality.
- Develop Inspection Protocols: For each control point, develop specific inspection protocols. This might include dimensional checks, material tests, or visual inspections. Determine what needs to be inspected, how it should be done, and the acceptable criteria for passing.
- Training and Resources: Ensure that staff are adequately trained in quality control procedures. This includes understanding how to perform inspections, how to use any relevant equipment, and how to report issues.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of quality control activities. This documentation should include inspection results, how discrepancies were handled, and any corrective actions taken.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update the quality control plan. Use feedback from the fabrication floor, clients, and any non-conformities to refine processes and improve quality.
Top Techniques For Quality Control In Sheet Metal Design
The design phase is where quality begins. Having a clear list of important quality metrics in sheet metal fabrication drawings sets the foundation for manufacturing efficiency. Some key design quality control techniques that design engineers use at this stage include:
- Detailed CAD Design: Precision in CAD drawings for sheet metal fabrication is non-negotiable. Ensure that every detail is accurately represented, as even minor discrepancies can lead to issues during fabrication.
- Layer Management: Organize different elements of the design into layers to enhance clarity and control. This simplifies the process of making modifications and ensures easy interpretation by the fabrication team.
- Annotation and Dimensioning: Clearly annotate dimensions, bend lines, and other critical details. This prevents misunderstandings and errors in the fabrication process.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material is fundamental to the success of the final product. Consider factors like strength, durability, weight, and cost to make informed decisions.
- Bend Simulation: Simulate the bending process using CAD software to predict potential issues like cracking or deformation, allowing for design adjustments before physical production begins.
- Stress Analysis: Perform stress analysis on the design to ensure the final product withstands operational loads and conditions, promoting durability and safety.
- Standard Parts Libraries: Utilize libraries of standard components to improve consistency and compliance with industry norms, speeding up the design process while ensuring quality.
- Detailed Drawings: Include all dimensions, bend lines, tolerances, and special instructions to guide the fabrication process accurately through comprehensive fabrication drawings.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): List all materials and components required for fabrication in a detailed BOM to ensure accurate procurement and inventory management.
- Drawing Review: Conduct a final review of the drawings for accuracy and to avoid costly errors during production.
- Standards Compliance: Ensure all drawings and models comply with relevant industry standards and regulations for both quality assurance and legal compliance.
- File Management: Maintain the integrity of design information with efficient organization and secure storage of CAD files, and proper version control.
- Peer Reviews: Conduct internal reviews of CAD drawings among team members for error detection and improvement suggestions, with a collaborative approach to quality.
- Client Feedback: Incorporate feedback from clients to ensure that the design aligns with their requirements and expectations.
- Nesting Software Integration: Use nesting software to optimize material utilization, reduce waste and cost, and for efficient production planning in the design phase.
- Transfer to Manufacturing: Ensure secure and accurate transfer of the final CAD files and documentation to the manufacturing team.
By diligently applying these sheet metal design, drafting and modeling techniques, design engineers can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and overall quality of sheet metal fabrication projects and meet both client expectations and industry standards.
Technology-Driven Approaches to Sheet Metal Drafting Quality Control
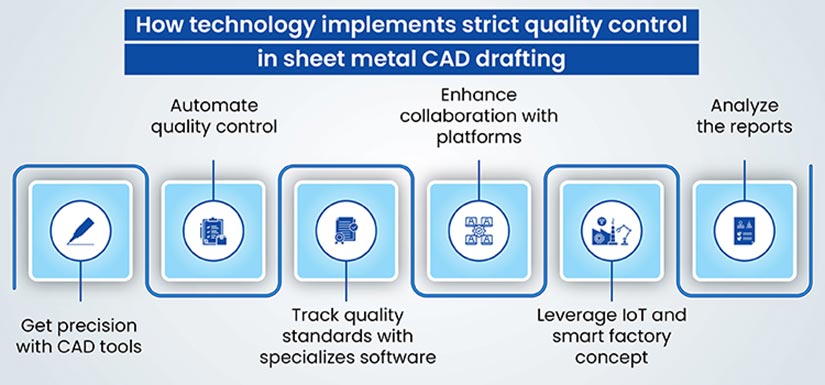
The use of suitable CAD platforms helps implement stricter quality control in sheet metal fabrication. The integration of technology streamlines processes and improves precision and consistency.
- Advanced CAD and CAM Tools for Precision: The use of advanced Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) tools is pivotal in sheet metal fabrication. These tools enable design engineers to create highly accurate and detailed models of the products. CAD software offers sophisticated features for detailed design, while CAM systems translate these designs into precise instructions for manufacturing equipment. This seamless transition from design to production minimizes errors and enhances the overall quality of the final product.
- Role of Automation in Quality Control Processes: Automation plays a crucial role in quality control. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with high precision and minimal error, making them ideal for tasks like dimensional checks, material handling, and even certain aspects of inspection. Automation also speeds up the production process, allowing for more consistent output and faster detection and correction of any deviations from the set standards. Automated machinery, equipped with sensors and feedback systems, can continuously monitor production parameters and make real-time adjustments to maintain quality.
- Software for Tracking and Maintaining Quality Standards: Specialized software solutions are available for tracking and maintaining quality standards throughout the sheet metal fabrication process. These systems can manage and analyze data from various stages of production, from initial design to final inspection. Quality Management Software (QMS) can integrate with CAD/CAM systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustment. They can track the performance of equipment, monitor the quality of incoming materials, and ensure that all processes adhere to predefined standards. Additionally, these tools can facilitate root cause analysis when defects occur, helping to prevent future occurrences.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Modern software tools offer advanced data analytics and reporting capabilities. By analyzing data collected throughout the fabrication process, these tools can identify trends, predict potential quality issues, and provide insights for process improvements. This data-driven approach enables proactive quality control, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring continuous improvement in production processes.
- Integration with IoT and Smart Factory Concepts: The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the manufacturing process, leading to the concept of a ‘smart factory’, is revolutionizing quality control in sheet metal fabrication. IoT devices can collect and transmit data in real-time from various points in the production line. This data can be used to monitor machine performance, track the progress of jobs through the factory, and ensure that every piece meets the set quality standards.
- Collaborative Platforms for Team Coordination: Technology also facilitates better communication and collaboration among team members. Collaborative platforms can ensure that everyone involved in the fabrication process, from designers to floor managers, has access to the latest information, designs, and feedback. This coordination is crucial for maintaining quality standards and swiftly addressing any issues that arise.
Technology in sheet metal fabrication detailing not only enhances the precision and quality of the products but also contributes to efficiency and cost-effectiveness in production. By embracing these technological advancements, companies can stay competitive and consistently deliver high-quality products to their clients.
Start your journey towards sheet metal fabrication excellence.
Explore how our sheet metal drafting experts add value to your designs.
Compliance with Industry Standards and Certifications
Compliance with industry standards and certifications is not just a regulatory requirement but a strategic advantage. Adhering to these standards ensures that products are safe, reliable, and of high quality, which in turn enhances market competitiveness. Let’s explore the importance of these standards and the process of obtaining and maintaining relevant certifications.
-
Need for Compliance for Market Competitiveness: Compliance with industry standards is crucial for businesses looking to establish and maintain a competitive edge in the market. It demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety, which are key considerations for clients. Moreover, compliance often opens doors to new markets and clients who require adherence to specific standards. It also minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhances the brand reputation, positioning the company as a reliable and trustworthy partner in the industry.
-
Overview of Relevant Industry Standards: Several industry standards are relevant to sheet metal fabrication, each catering to different aspects of the process:
- TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association): TEMA standards are crucial for the design and construction of heat exchangers, providing guidelines on tolerances, materials, and fabrication practices.
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute): ANSI standards cover a wide range of product quality and safety guidelines, including those relevant to sheet metal fabrication.
- IS (International Standards): These standards, including those from ISO (International Organization for Standardization), provide global benchmarks for quality, safety, and efficiency.
Compliance with these standards ensures that products meet the highest levels of quality and safety, which is essential in a global market.
-
The Process of Obtaining and Maintaining Certifications: Obtaining and maintaining certifications like SDI (Steel Door Institute), SolidWorks, and Autodesk requires a dedicated approach:
- Initial Assessment and Training: The first step involves an assessment of current processes and training of personnel to meet the required standards.
- Documentation and System Implementation: Developing comprehensive documentation and implementing systems that align with the standards.
- Certification Audit: Undergoing an audit by a certified body, which assesses the compliance of processes and systems with the standards.
- Continuous Improvement and Recertification: After obtaining certification, companies must engage in continuous improvement and regular audits to maintain their certification status.
The HitechDigital team, for instance, has certifications in SDI, SolidWorks, and Autodesk. These certifications attest to their expertise and adherence of industry-leading practices, providing an added layer of trust and reliability for their clients.
- Regular Updates and Training: Regular training and updates ensure that the team remains compliant and that the certifications retain their value.
Compliance with industry standards and obtaining relevant certifications are critical for any sheet metal fabrication company aiming to thrive in the global market. Companies like HitechDigital, with their range of certifications, set a benchmark in the industry, demonstrating the value of these accreditations in achieving business excellence.

How AI is impacting design development for sheet metal fabrication
- Optimize CAD design process with AI for metal fabrication
- Accelerate prototyping; ensure quality and compliance with AI
- Reduce scrap and minimize environmental footprint
How Expert Sheet Metal Cad Drafting Teams Solve QC Challenges
An expert sheet metal CAD drafting team, like the one at HitechDigital, helps in addressing the common challenges of quality control in sheet metal fabrication. By implementing best practices and leveraging their extensive experience, these teams can significantly mitigate issues related to cost-quality balance, meeting delivery timelines, and managing client expectations. HitechDigital’s approach, as outlined here, illustrates this.
- Adherence to Best Practices: HitechDigital’s team follows a set of well-defined best practices that are crucial in maintaining high-quality standards while addressing the typical challenges in sheet metal fabrication:
- Comprehensive Planning and Analysis: Before initiating any project, the team conducts thorough planning and feasibility analysis. This ensures that all potential issues are identified and addressed early in the process, reducing the risk of costly errors and delays.
- Regular Training and Skill Upgradation: The team undergoes regular training to stay updated with the latest CAD technologies and industry standards. This continuous skill enhancement allows them to handle complex projects efficiently and accurately.
- Utilization of Advanced CAD Tools: By employing state-of-the-art CAD tools, the team achieves high precision in drafting, which is crucial for maintaining quality and reducing rework.
- Effective Communication Protocols: HitechDigital emphasizes clear and continuous communication within the team and with clients. This ensures that client requirements are fully understood and met, and any changes or issues are promptly addressed.
- Case Studies Demonstrating Success: HitechDigital’s approach is best illustrated through specific case studies:
- Case Study 1: Cost-Quality Balance for a Custom Enclosure Project: In a project involving the design of custom enclosures, HitechDigital’s team used advanced simulation tools to optimize material usage and reduce waste. By doing so, they managed to lower costs without compromising the structural integrity and quality of the enclosures. This project demonstrated how innovative solutions could achieve cost efficiency while maintaining high-quality standards.
- Case Study 2: Meeting Tight Deadlines for a Large-Scale Fabrication Project: For a large-scale project with a tight deadline, the team implemented a streamlined workflow and parallel processing. By dividing the project into smaller, manageable sections and working on them simultaneously, they managed to complete the project ahead of schedule, maintaining the highest quality standards.
- Case Study 3: Exceeding Client Expectations in a Complex Custom Fabrication: In a project involving complex custom fabrication, HitechDigital’s team engaged in early-stage consultations with the client to fully understand their unique needs. They provided regular updates and incorporated feedback efficiently, resulting in a product that not only met but exceeded the client’s expectations.
Thus, the presence of an expert sheet metal CAD drafting team like HitechDigital eliminates common challenges in quality control through best practices, advanced tools.
Future Trends and Innovations in Quality Control
As we look towards the future, several emerging trends and innovations are set to redefine the standards and practices of quality control in the industry.
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML can predict and detect quality issues before they occur by analyzing patterns in data collected from manufacturing processes. AI algorithms will become a routine part of quality control as they can also optimize fabrication processes for quality and efficiency, reducing waste and improving consistency.
- Advanced Sensors and IoT: The integration of advanced sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT) in fabrication equipment will enable real-time monitoring of production processes. This technology can track everything from material quality to environmental conditions, ensuring that each stage of fabrication meets quality standards.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: While traditionally used for prototyping, 3D printing is increasingly being adopted for production in sheet metal fabrication. This technology allows for more complex designs and can potentially reduce errors and material waste, enhancing overall quality.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies can be used for training purposes and to simulate fabrication processes. This can help in identifying potential quality issues in the design phase, reducing the risk of errors during actual production.
Predictions for Future Quality Control Methodologies in the Industry:
- Predictive Quality Control: Future quality control is likely to be predictive rather than reactive. By leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, manufacturers will be able to anticipate and prevent defects, leading to higher quality standards and reduced rework.
- Customization and Personalization: As customer demand more customized and personalized products, quality control processes will need to become more flexible and adaptable. This will involve modular design principles and flexible manufacturing systems.
- Sustainability and Quality Control: There will be a growing emphasis on sustainability in quality control. This will involve the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient processes, and recycling of waste. Sustainable practices will factor heavily in quality assessment.
- Integration of Quality Control in Supply Chain: Quality control processes will extend beyond the manufacturing floor and integrate more closely with the entire supply chain. This will ensure quality in raw materials, manufacturing processes, and final product delivery.
Conclusion
The move towards predictive quality control methodologies underscores a proactive approach, focusing on preventing defects rather than merely detecting them.
For sheet metal fabrication companies, these advancements present both opportunities and challenges. Staying abreast of these changes, investing in new technologies, and continuously upskilling are necessities for maintaining competitiveness and meeting the evolving demands of clients.
Manage your shop drawings quality proactively
Explore our predictive sheet metal CAD drafting quality control techniques