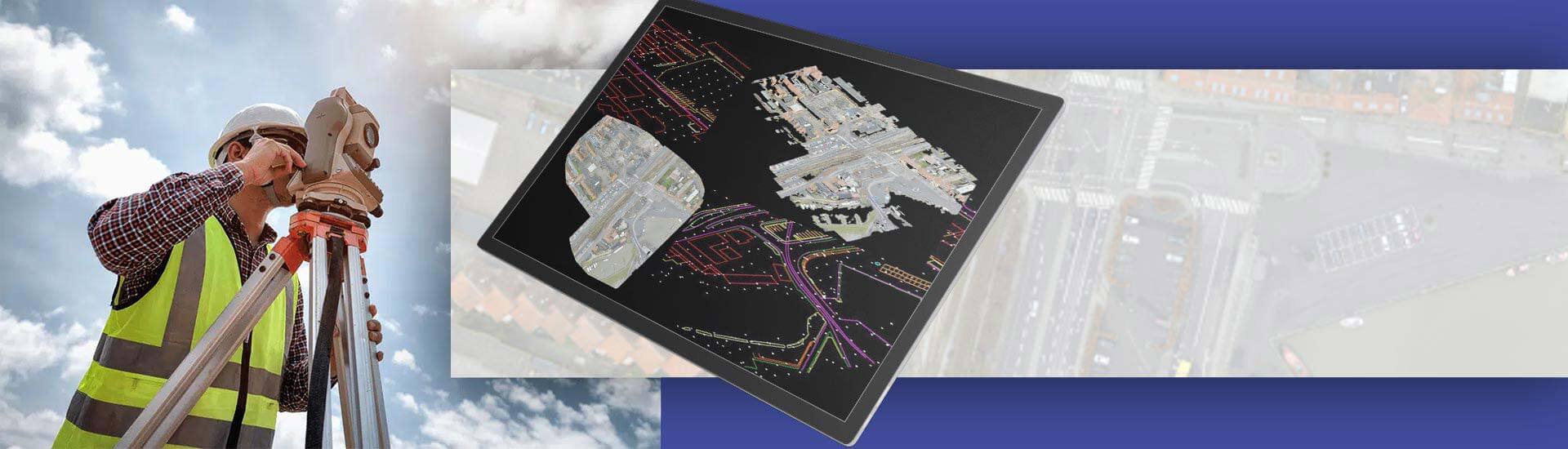
- Land surveying helps to gather detailed knowledge of topography, boundaries and site surroundings.
- Given the speed and scale of modern construction projects, use of traditional surveying techniques creates too many bottlenecks and errors.
- Surveyors have adopted 3D laser scan to CAD drafting as the go to method for precise and in-depth site survey and analysis.
- 3D laser scanning and site mapping on a digital platform has become the choice method for terrain investigations and site development.
Table of Contents
- A brief overview of 3D laser scanning
- An opportunity to understand traditional land surveying vs. 3D Laser Scanning
- A breakdown of land survey CAD drafting: From a scan to usable plans
- 4 key advantages of 3D laser scanning for surveying
- Point Cloud to CAD: presenting raw scans into design reality
- Comprehending the role of a laser scanning surveyor
- Cost & practical considerations for survey projects – a quick snapshot
- The influence of AI / automation in point cloud to CAD and feature extraction
- Conclusion
Surveying firms chart spaces and plot exact lines to represent a site or property so it can be assessed for development. Land surveying lets us decide how to align roads, plot and build within a site. The survey data helps architects and contractors to determine opportunities and limitations in construction planning on a site. And when these plans are built to correct specifications project execution becomes smoother.
In modern projects, traditional surveying techniques have been mostly discarded due to inaccuracy and because they don’t work well with digital setups. Also, with traditional methods of surveying, both storing and sharing data is hard, and it becomes difficult to keep all plans up to date.
For surveying companies today, point cloud to CAD conversion is the first choice for clean and fast digital mapping of site conditions. Laser scanning helps site crews avoid multiple site visits and eliminates guesswork.
Scan data provides complete accuracy, and plans built on such data are also highly reliable. Even the smallest edges can be documented with laser scanning, and that’s how scanners have entirely changed how surveys are done.
A brief overview of 3D laser scanning
Surveying teams use 3D laser scanning equipment to measure how long it takes for a laser pulse to strike a surface and return. This is done by software in the scanner, which converts those timings into dimensions. Each return trip generates a data point, and ultimately we have point clouds capturing millions of points that show up the spaces, edges and shapes.
Specialized 3D laser scanning services with CAD drafting are usually employed to document site details with high accuracy for any project. These firms are experts at measuring edges, curves and heights using laser scanners. Every scan helps to solve part of the puzzle to digitally reconstruct physical spaces, and the 3D model built from the scan data becomes a central platform for designs and audits. It helps project teams clearly visualize problems and resolve them with accuracy.
The site data carried by point clouds comes in a raw format and has to be processed before it’s fit for use in designing with CAD software. So first raw scans are converted into lines, layers and shapes for clarity. Details are traced for complete accuracy as raw data speaks with the physical structure. As a surveyor it helps you create surveys, maps and CAD drawings that are fully reliable for downstream work.
An opportunity to understand traditional land surveying vs. 3D Laser Scanning
While we have discussed 3D laser scanning in the above sections, it’s time to breakdown how it outperforms old land surveying processes.
| Feature | Traditional ways | 3D laser scans | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Time-consuming based on manual audits. | Quick scans document data in minutes. | Projects including highways and mapping. |
| Precision | Human errors and restricted detail. | Highly-dense and precise. | Analyze structural details and perform quality checks. |
| Data processing | Drawings and notes are stored in silos. | Digital data is easy to store and share. | Cloud storage along with BIM integration. |
| Range | Misses hidden areas. | Captures every corner of the space. | Used for tunnels, plants, and bridges. |
| Deliverables | Preliminary sketches and maps. | In-depth 3D models for analysis and design. | Facilitate retrofitting, design validation, and as-built results. |
Convert site scans into accurate and clean CAD drawings to match every object.
Remove guesswork and stay away from wasted time.
A breakdown of land survey CAD drafting: From a scan to usable plans
As a professional outsourcing firm, we convert laser scan data into 2D or 3D CAD drawings. We turn your concepts into implementable designs that connect layers, shapes and lines with complete accuracy. Our tools, teams and infrastructure help to plan, edit and share designs without any loss of integrity.
Explaining the Scan to CAD workflow
If you’re a surveying company, it’s crucial for you to understand the Scan to CAD workflow. It’s used to convert the data from raw scans into models that guide design, planning and construction.
-
1. Laser scans:
Scanners are used to document precise site data and surfaces’ data in digital point clouds.
-
2. Process data:
The raw point cloud data is cleaned, aligned and filtered to exclude noise, and then validated for downstream use.
-
3. Convert to CAD format:
Cleaned point clouds are converted into CAD models that can be edited and detailed in software.
-
4. Verify designs:
Design dimensions, layouts and other attributes are checked for compatibility against the actual site conditions.
-
5. Coordinate projects:
Coordination using a centralized data model prevents rework, saves time and maintains design consistency across trades.
Preserving details with Scan to CAD
As a Scan to CAD specialist company, we diligently preserve fidelity of site data and make sure every edge and surface in the model matches actual as-built conditions. We make sure that when the point cloud is ultimately converted to CAD formats, we can rely on its accuracy. The accurate model helps teams with design, auditing and refinement in depth.
Assessing alignment and QC as a laser scanning surveyor
As a surveyor using laser scanners, you know you need to align scans with real coordinates. You have to check overlaps, change angles and validate accuracy of the scans. All of these need be done before 3D modeling begins.
4 key advantages of 3D laser scan to CAD drafting
As a surveying company, you can use numerous advantages to attain control and quality. We see each in a brief form for simplicity of understanding.
-
1. Accuracy and dense data capture:
Document every curve and edge with millions of points clouds. It makes sure correct dimensions for site measurements.
-
2. Collect vast data in shorter timelines:
Every scan is capable of a large dataset that charts real details for 3D modeling, analysis and documentation.
-
3. Safety advantages for a risky terrain:
Scan areas that pose risks while they’re accessed. It helps you capture data from a safe distance to eliminate human risks.
-
4. Digital documentation for verification:
You can easily verify scanned data vs actual conditions to look for deviations, check alignment and maintain QC for the overall project.

Unlock the Power of Point Cloud to BIM: Strategies for Successful Implementation
- Establish an accurate geospatial context for point cloud data.
- Simplify and optimize mesh representations of point clouds.
- Implement rigorous quality control procedures throughout the process.
- Adopt an iterative approach to modeling based on ongoing analysis.
Point Cloud to CAD: Presenting raw scans into design reality
Design reality is the ultimate outcome, but it requires the right toolset, best practices and deliverables as a complete package.
1. Software tools and techniques in point cloud to CAD
We can help you convert your points clouds to CAD using Revit, ReCAP and AutoCAD. Design-ready models make sure segmentation, alignment and surface fitting. Scans are refined into precise geometry that helps surveyors create CAD models which are quickly editable and reflect conditions of the real world.
2. Clean, filter, align and classify data
Point cloud data requires cleaning to eradicate noise and clutter. When data is filtered it provides clarity and required details are left in the 3D model. Multiple scans are aligned into a single model, while floors, pipes and walls are classified into categories. The following steps prepare the data for accuracy, organization and CAD conversion.
3. Prepare deliverables like 2D maps, contour models and 3D terrain models
Surveyors can use 2D maps created by specialists to show the scale and layout which is ideals for boundary checks and site plans. Preparing contour models shows the shape of the land and elevation that illustrates drainage and grading. Terrain models document surfaces and slopes for planning, design and estimation of earthwork.
Scan to CAD drafting for landscaping and road mapping in Europe
 Overall project site
Overall project site
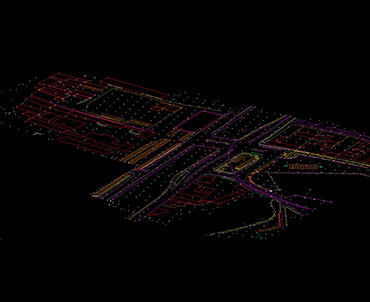
 Point cloud Arial View of Project site
Point cloud Arial View of Project site
 3D Vector Drawing View
3D Vector Drawing View
A surveying firm from Europe couldn’t create 3D drawings and extract data on terrain, roads, outlines, etc. We discussed the project with the client and understood their Scope of Work(SOW) and even assessed their obstacles. The quality of the input was inferior and it didn’t provide the delineations. It also required a high level of accuracy across various project parameters.
We proposed a solution wherein images were converted into 3D vector CAD drawings. These drawings were enriched with polygons, polylines and other shapes. Annotations and labels were also added within the drawings. Our team quality checked the CAD documentation to make sure the field data aligned with the vector model. Once everything was done, the deliverables were sent to the surveyor.
The results were:
- Higher accuracy and quality of the final output
- Time and cost savings of 20% using effective scheduling
- Seamless survey process with lower iterations
- Smart decisions for energy efficiency and sustainability
Comprehending the role of a laser scanning surveyor in Scan to CAD drafting
As a laser scanning surveyor you have roles and responsibilities including planning field strategies, capturing data, coordinating with teams and ensuring quality control. We have broken down each into the following:
-
1. Devise strategies and plan scans:
Before scanning starts, the surveyor needs to plan the scan area and its sequence.
It makes sure greater coverage, reduces blind spots and leads to better data capture in confined spaces.
-
2. Capture data, registration and checking:
Once the data is captured it needs to be cleaned, filtered and aligned to form a single model.
Accurate alignment makes sure every measurement taken is consistent across the project.
-
3. Coordinate with CAD/design teams:
You work closely with design and CAD teams to make sure data aligns with project requirements.
It keeps dimensions precise, prevents rework and refines project processes.
-
4. Enable quality control and validate:
Verify scan accuracy by comparing design models with scan data or control points.
Validate precision, check errors and maintain the highest standards through continuous audits.
Cost & practical considerations for survey projects with Scan to CAD conversion – a quick snapshot
Survey projects are surrounded by complexities, large scale and risks. Here we consider a few:
1. Factors affecting cost (site size, complexity, deliverables):
Large areas require meticulous planning and various scan setups to document the entire area. Tight spaces need advanced techniques to capture masked data. As a surveyor, you need to pay close attention to the deliverables – be point clouds, 3D BIM model or CAD drawing. It relies on design, documentation and construction validation.
2. Turnaround time and efficiency gains:
Laser scanners document in-depth site data and are less time consuming than manual measurements. This creates faster turnarounds as site visits and manual work is greatly reduced. Often, visits are made only when the scans show discrepancy that needs resolution and manual verification.
3. When it makes sense to hire a survey scanning service:
If you’re a surveying firm facing challenges in scanning sites, it’s wise to use the right toolset along with experience and QC. This is when scanning services help you to make the most of modern methods.
The influence of AI / automation in Scan to CAD and feature extraction
In the future, the usability of Scan to CAD models will depend on the capability of AI and automation. AI is continuously developing to help surveyors and other participants identify and extract features with full precision.
With this, automation will help you clean, align and categorize data, expediting project handovers. As AI continues to learn from scans, it’ll develop databases to identify patterns, simplify complex geometries and make sure of clean CAD outputs.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning has made it possible for surveyors to quickly map sites of any size and do detailed site analysis. Planning has become easier and more accurate when using a 3D model built from scan data, and which captures all details of terrains, structures and other spaces. This has helped improve designs while cutting down on onsite visits.
Often now, survey firms delegate Scan to CAD drafting to external experts like us to scale up and also speed up projects without losing accuracy or data integrity. This improves collaboration between distributed teams as usually outsourcing companies have robust setups for remote team collaboration. This improves surveying outcomes as surveyors, engineers and designers can all share a single source of truth.
Are you tired tracing over raw scans that do not line up ?
Get Scan to CAD services that make designs your reality.







