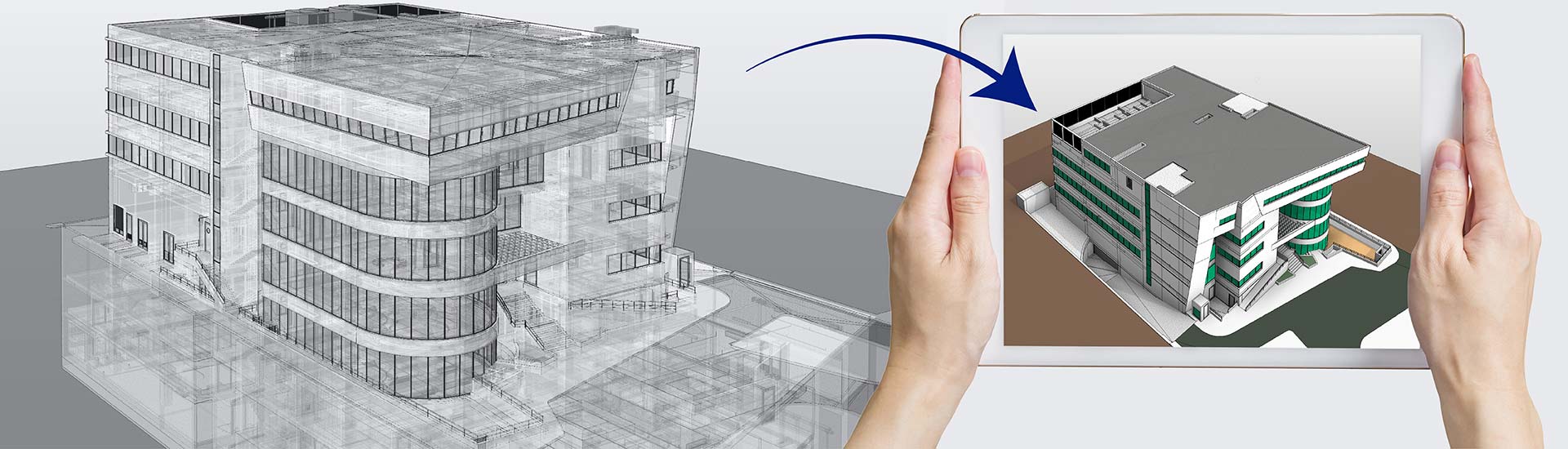
- Project complexities and intricate geometry of modern construction, renovation, and retrofitting shifting from simple Scan-to-BIM processes to AI and automation.
- AI and automation-driven Scan-to-BIM benefit surveyors and various project stakeholders with greater accuracy, lower manual effort, cost savings, and quick data processing.
- Advancements in Scan-to-BIM including AI, automation, AR/VR, Digital Twins, and other trends that will carve a future for Point Cloud to BIM services.
Table of Contents
Traditional Scan-to-BIM workflows face significant challenges that impact project outcomes. When surveyors rely on conventional scanning software and technologies, data accuracy suffers, resulting in erroneous point cloud to BIM conversion and defective 3D BIM models. The manual processing of extensive point cloud datasets drains resources and significantly extends project timelines. Without automation, surveyors must manually handle Scan-to-BIM modeling and feature extraction, leading to errors and inconsistencies that affect all project stakeholders.
The solution lies in emerging trends in Scan to BIM technology. AI-driven automated modeling and object recognition are being quickly adopted by Scan to BIM services to address these legacy challenges. These technological advancements enable the creation of precise Scan-to-BIM models while establishing seamless workflows and enhanced collaboration among team members.
This technological evolution in Scan-to-BIM, incorporating automation, AI, and cloud computing, drives greater efficiency, reduces costs, and delivers superior project outcomes in construction, renovation, and retrofitting projects. The result is a more resilient, sustainable and cost-effective building process that meets modern construction demands.
The role of AI in Scan to BIM advancements
Converting point cloud data to BIM models becomes faster and more accurate with artificial intelligence (AI). AI-powered automation handles key tasks like object recognition, model creation, and classification. Automation reduces manual effort while improving workflow efficiency. Project teams can gain higher precision in their BIM models generated from scanned point cloud datasets.
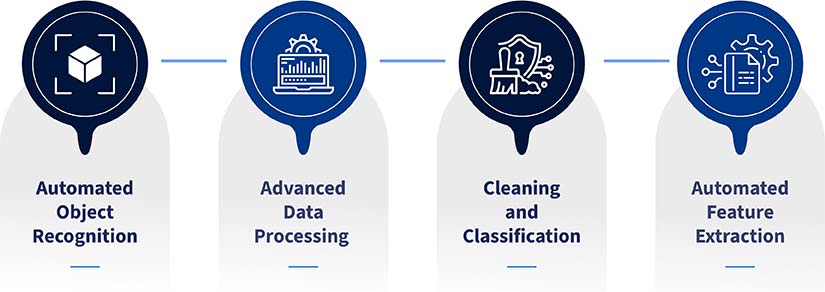
- Automated object recognition: AI algorithms are reshaping Scan-to-BIM by automating the identification and classification of architectural components enriched within point cloud data. Rather than manually labeling doors, walls, and windows, AI precisely identifies features that reduce time and effort for data analysis. The presence of automation makes the BIM modeling process seamless, ensuring a quick turnaround time and supporting surveyors and surveying firms’ focus on complex project activities.
- Advanced data processing: error mitigation: AI-powered tools, including Autodesk BIM360, SketchUp, Rhino, etc., are equipped to process large datasets and quickly identify anomalies and patterns that may be overlooked during manual reviews. Connecting Revit and Navisworks with AI-driven platforms can help scan-to-BIM modeling teams with object recognition for conversion into native Revit members. AI can also be used for model optimization and interference detection using Navisworks to prioritize clashes based on severity and project impact.
- AI-powered point cloud cleaning and classification: Machine learning (ML) algorithms are utilized to automatically clean and categorize scanned point cloud data. This includes the identification and removal of noise in the data, as well as classifying building elements like floors, columns and walls. AI-powered automation accelerates the creation of the Scan-to-BIM model and improves its accuracy by using clean and required data to create the required model.
- Automated feature extraction: AI helps with the automatic extraction of key features from point cloud data, including structural members, architectural details, and openings. This automation capability reduces the requirement for manual data processing, expediting the Scan-to-BIM modeling process, and mitigating the risk of problems caused by human intervention. Automating the extraction process enables the quick and efficient generation of 3D models.
Enhance construction workflows using Scan to BIM.
Use detailed As-Built data for faster clash detection and expedited project execution.
By adopting Scan to BIM best practices and integrating AI, the industry is achieving higher productivity and accuracy, which is critical for projects with stringent deadlines and quality requirements.
Automation: enhancing efficiency and accuracy
Point Cloud to BIM automation offers major benefits through improved accuracy and efficiency in scan-to-BIM workflows. Project teams can gain enhanced capabilities in object recognition, point cloud processing and 3D model creation. The reduced need for manual surveyor effort leads to faster project schedules while maintaining precision. This automated approach helps minimize errors and generates more reliable scan-to-BIM models.
- Automated point cloud segmentation: Advanced tools can automatically segment point cloud data into logical elements like ceilings, floors, and other structural elements. The presence of automation mitigates the requirement for manual element classification, leading to lower labor costs and faster project schedules.
- Streamlined workflows for large-scale projects: Scan-to-BIM enriched by automation workflows enables quick and simultaneous processing of various datasets, making Point Cloud to BIM flexible and scalable for complex and large structures. This provides high value in infrastructure projects and urban planning that require advanced 3D modeling techniques to execute intricate geometry.
- Integration with prefabrication: Automated scan-to BIM processes can convert point cloud data into actionable information for modular construction and prefabrication. This fosters the accurate manufacturing of building elements, leading to fewer errors, optimized material use, and sustainable construction.
The following case studies provide real-world applications of scan-to-BIM. Based on these case studies, surveyors can understand business needs, challenges, advantages, and solutions while leveraging Point Cloud to BIM for construction and renovation.
Point cloud scans converted to a 3D As-Built model with +-10 mm accuracy improves cost-efficiency for a commercial project.

A US-based architecture firm approached HitechDigital for a commercial project in the US. Point cloud scans were provided as input to create the model and As-built documentation. Low-quality input scans and large file sizes with redundancies were challenges the team at HitechDigital had to face.
Based on input scans and 360 photos, the team generated a Revit model at LOD 300-400 with As-Built drawings and a set of PDF files containing elevations, building sections, and floor plans.
The final deliverables handed over to the client led to –
- Cost optimization based on accuracy and efficiency
- 95% FTR deliverables
- Faster completion within a timeline of 2 months
 Point Cloud to As-built Model
Point Cloud to As-built Model
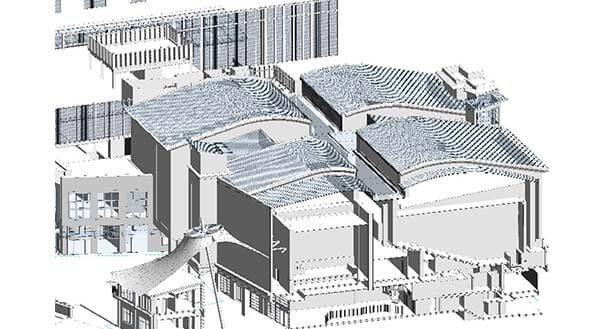 Point Cloud Data to Revit Model
Point Cloud Data to Revit Model
Innovations beyond AI and automation
Beyond AI and automation, advancements, including AR/VR, real-time data analytics, cloud-based processing, etc. are enhancing data accessibility, data sharing, and decision-making in Point Cloud to BIM.
- Advanced Laser Scanning Technologies: Upgrades in laser scanning technology led by greater accuracy, speed, and reliability are driving Scan-to-BIM innovation. These enhancements enable accelerated data acquisition, high-resolution point clouds, and faster access to congested areas, resulting in detailed and comprehensive Scan-to-BIM models.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration: Cloud platforms like BIM360 foster seamless collaboration and data sharing between multiple project participants in Point Cloud to BIM workflows. This provides surveyors and users with real-time point cloud data access, 3D BIM models, and project data. This leads to enhanced communication, coordination, and data-driven decision-making for the entire project lifecycle.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): AR/VR tools improve visualization and understanding of Point Cloud to BIM information. By immersing users in a virtual environment or overlaying digital data on the real-world, AR/VR facilitates the intuitive use of point clouds and 3D BIM models. This enhances design reviews, interference detection and collaboration.
- Digital Twins: Scan-to-BIM is an integral element in generating digital twins, which are versatile replicas of physical assets. By integrating real-time information from sources such as sensors, digital twins deliver a comprehensive and updated view of the As-Built space. This enables improved asset management, performance optimization and predictive maintenance for facilities managers.
- Real-time data analysis: Real-time data analysis tools are a vital component in Scan-to-BIM by providing quick insights and feedback during scanning and modeling. This leads to the preemptive identification of potential problems, enhanced quality control, and effective on-site decision-making.
- Automated feature extraction: AI-driven algorithms can extract key components from point cloud data, including doors, walls, and structural elements. This reduces manual intervention and expedites BIM modeling processes, enabling a quick project turnaround.
- Improved interoperability: Standardized and open BIM formats improve interoperability in Point Cloud-to-BIM workflows. This supports streamlined data exchange between various stakeholders and software. It enhances collaboration and reduces the risk of errors and potential issues.
Challenges in 3D Scanning for BIM Integration
Challenges in 3D scanning for BIM integration include obstructions and occlusions that can impede complete data capture. Variations in lighting and surface reflectivity affect scan quality and the requirement to process data and operate equipment.
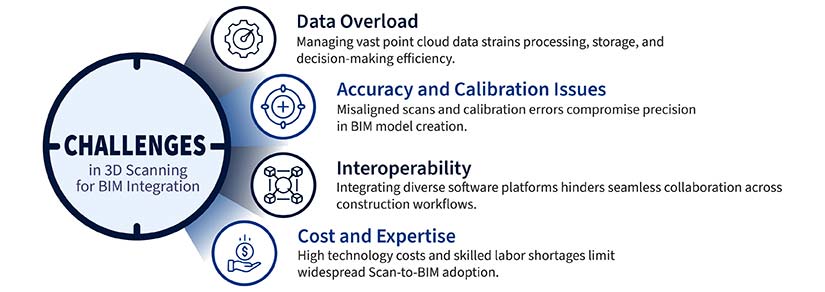
- Data overload: 3D scanning generates large datasets, which leads to challenges in managing, processing and analysing data. It also provokes data overloads, which can lead to disconnected data management.
- Accuracy and calibration issues: Calibration issues, environmental factors, and scanning technology limitations can introduce errors, necessitating careful planning, accurate execution, and stringent quality control steps.
- Interoperability: Seamless data exchange between BIM platforms and scanning tools is necessary. Interoperability obstacles arise from multiple data formats and software compatibility, requiring the utilization of conversion tools and standardized formats to ensure quick data integration.
- Cost and expertise: Implementing 3D scanning tools and workflows for BIM integration incurs costs related to software, equipment and personnel. The need for tailored expertise in working with scanning equipment, data processing and integration with BIM models poses an obstacle for projects.
The future of Scan to BIM: what lies ahead
The integration of AI, automation, and emerging technologies in Scan to BIM is setting new benchmarks in the AEC industry. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-driven predictive analytics: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reforming Scan-to-BIM through predictive analytics. AI algorithms can help assess real-time and historical data to predict structural problems, maintenance requirements and potential risks before they manifest on-site. This preemptive technique improves decision making, reduces delays, and enhances project results. Moreover, machine learning (ML) models can refine accuracy for object classification and feature extraction, enabling smarter scan-to-BIM models.
- Greater adoption of robotics: Robotics will play an important role in Scan-to-BIM by automating data capture with greater accuracy and speed. Ground-based and autonomous drones or robots will be equipped with AI-driven sensors and LiDAR for large and complex projects. This reduces human intervention, enhances safety and improves precision in challenging projects.
- Sustainability and green BIM: Sustainability is a key focus, and Scan-to-BIM supports green initiatives. AI-driven scan-to-BIM models assess energy performance, optimize material efficiency, and contribute to a lower carbon footprint. From improving natural lighting to reducing waste for renovation or retrofitting projects, Scan to BIM is driving sustainable construction practices. Green BIM is crucial in ensuring sustainability and compliance in building design.
Conclusion
The rapid advancements in Scan to BIM services are revolutionizing the AEC industry by enabling high-detail 3D modeling in architecture, seamless workflows, and the digital reconstruction of complex structures. While challenges like data processing and interoperability remain, emerging technologies such as AI, automation, and digital twins are poised to overcome these hurdles. By embracing these innovations, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of Scan to BIM advancements and redefine the future of construction.
For organizations seeking to stay ahead, investing in emerging technologies in Scan to BIM is not just an option, but a necessity. The journey toward smarter, more efficient and sustainable construction begins here.
Maximize project efficiency with Scan to BIM workflow and tools.
Transform laser scans into actionable data for real-time 3D modeling and error reduction.







