- The demand for energy-efficient, cost-effective, and comfortable building spaces requires accurate HVAC design
- HVAC system design faces obstacles including inaccurate load estimates, oversizing/under sizing, and achieving sustainability requirements
- Customized HVAC solutions driven by accurate load calculations and advanced tools enable enhanced system sizing, improvements in energy efficiency, and cost reduction
Table of Contents
- Internal and external factors that affect HVAC design
- HVAC load calculation benefits in modern building systems
- Common mistakes in HVAC load calculations
- How are HVAC load calculations performed?
- Tools and software used for HVAC load estimation for efficient HVAC design and installation
- Successful case studies in HVAC design and construction
- Transforming HVAC load calculations for future-ready smart buildings
- conclusion
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems like air conditioners, diffusers, heat pumps, furnaces, etc. play a key role for HVAC designers and engineers in preserving temperature, indoor air quality, and humidity in buildings. Accurate and data-rich HVAC design regulates environmental conditions to realize required health conditions and comfort while sustaining energy efficiency. These systems are crucial for both residential and commercial construction projects.
Inaccurate HVAC load calculations can lead to inefficient HVAC design and installation. Undersized systems struggle to achieve occupant comfort, while oversized HVAC systems reduce lifespan and cause energy waste. These scenarios lead to inconsistent humidity, temperature and greater energy costs.
Achieving precision in HVAC design services leads to a reduction in energy consumption, optimal performance, and operational costs. Accurate HVAC system sizing improves occupant comfort through consistent air and temperature quality. Design precision also enhances the building lifespan, reduces wear and tear, and prevents untimely breakdowns, contributing to greater efficiency.
Customized HVAC solutions support architects in integrating HVAC systems into building layouts without compromising aesthetics. Engineers can use HVAC load calculation services to enhance system performance while complying with sustainability goals and system performance. Contractors can use accurate HVAC specifications that accelerate installation, reduce errors, and ensure compliance with industry building standards. Offering tailored solutions improves coordination between professionals to enhance building efficiency and build high-performance HVAC systems.
In this article, we discuss the importance of HVAC load calculations in building design. We explore how precise HVAC load estimation plays a key role in improving system efficiency, longevity, and comfort. This article also covers common mistakes, benefits, key steps and tools utilized in HVAC load estimation. Moving forward, we also focus on successful case studies and new technologies that can enhance HVAC load calculations in building design.
Internal and external factors that affect HVAC design
An HVAC load calculation estimates the thermal energy needed to achieve an optimal indoor environment. HVAC designers and engineers need to calculate the heating and cooling loads for every space in the building. Considering factors such as building orientation, insulation, building materials, internal heat sources, and external weather conditions, HVAC engineers can use the right equipment to help with higher energy efficiency and performance improvements. HVAC load estimation sets the foundation for designing an HVAC system that sets the balance between functionality, comfort and energy usage.
Heat gain and loss refer to the measure of thermal energy that enters or leaves a building. Heat gain relates to sources such as sunlight that enters through windows, electrical systems, and occupant activities. Moreover, heat loss occurs through inadequate insulation within doors, walls, windows and infiltration. These factors critically affect the temperature required for a building project. Heat gain is significant for cooling load calculations, while heat loss relates to heating load calculations. These factors balance the HVAC system to manage indoor occupant comfort.
Industry standards, including ASHRAE, provide comprehensive guidelines to calculate HVAC load. These standards insure calculations are precise, consistent, and latch on to best practices for multiple building types and climate settings. These ASHRAE guidelines provide tools and methodologies that support HVAC design engineers to meet comfort requirements and energy efficiency needs. It ensures enhanced performance in multiple conditions.
HVAC load calculation benefits in modern building systems
Accurate HVAC load calculations lead to enhanced system sizing, improved energy efficiency, and a reduction in operational costs. Maintaining consistent humidity levels and temperatures improves occupant comfort. Moreover, precise load estimation reduces initial and long-term costs, which contribute to energy-efficient and sustainable building.
Enhanced energy efficiency: Minimizing oversizing or under sizing systems
Accurate HVAC load estimation supports HVAC engineers in designing and engineering HVAC systems that are undersized or oversized. Manufacturing and installation of oversized HVAC systems leads to energy waste and produces inefficient cycles, while undersized equipment struggles to meet the required demand. HVAC load calculation benefits engineers and stakeholders with lower energy consumption, reduced utility costs and higher operational efficiency.
Improved occupant comfort: Maintaining optimal indoor temperature and humidity levels
A precise and efficient HVAC design process ensures stability for an indoor climate setting through the accurate determination of heating, cooling, and ventilation. This mitigates temperature fluctuations, lowers humidity or inadequate airflows, which creates a consistent comfortable environment. A well-designed HVAC system improves the occupant comfort, productivity, and overall quality of the indoor environment. This ensures complete comfort with minimal energy waste.
Reduced upfront costs by selecting appropriate system sizes
Accurate HVAC design and installation prevents unnecessary expenses from oversized systems and ensures a cost-effective performance. Furthermore, an optimized performance lowers energy consumption, which mitigates higher utility bills and reduces maintenance costs. HVAC design services support the creation of properly sized systems that lead to lower wear and tear, minimal repairs, and longer equipment life.
Common mistakes in HVAC load calculations
Common HVAC load calculation errors include issues with building orientation and insulation. This leads to inaccurate system sizing. Ignoring parameters, including internal heat gains and climate changes, lowers efficiency. Inaccuracies in calculations lead to lower performance issues and greater operational costs for owners and maintenance personnel.
Examples of errors (e.g., reliance on rules of thumb, overlooking latent loads)
Dependence on the rules of the thumb or general data for load calculations leads to inaccuracies in sizing systems. Ignoring latent loads like humidity control provokes systems to underperform, which leads to discomfort. Neglecting factors such as insulation or building orientation compromises the accuracy of these calculations.
Consequences of inaccurate calculations: Energy inefficiency, equipment failure, and comfort issues
Inaccurate HVAC calculations lead to inefficiencies, while systems need to overperform to meet the required demands. This raises energy costs. An inaccurate HVAC design causes overloading or frequent cycling, which leads to expensive repairs, inconsistent temperature, and reduces overall satisfaction.
How are HVAC load calculations performed?
HVAC load estimation requires the calculation of heating and cooling needs based on parameters such as climate, insulation, and building size. Key steps to calculate accurate HVAC load calculations include heat loss/gain, ventilation requirements, and occupancy patterns. Tools, including Manual J or software like ASHRAE guidelines or Carrier HAP ensure an accurate HVAC design process.
Surveying building specifications and usage
This includes collecting accurate and detailed information about the buildings’ layout, size, materials, and purpose. Key aspects include window placement, building insulation and roof types. A thorough understanding of these spaces will be utilized to support the calculation of heating and cooling needs. Furthermore, the identification of occupancy patterns and HVAC equipment like furnaces, ACs, heat pumps, etc. leads to detailed load calculations. Thorough surveys ensure the HVAC load estimation is customized to perform based on requirements.
Evaluating external environmental conditions
Evaluating external conditions is a crucial step in HVAC load calculations. Parameters like temperature variations, local climate, wind patterns, and humidity affect heat loss or gain. Building orientation, surrounding spaces, and natural shading can impact solar radiation through walls and windows. Evaluating these conditions helps determine accurate cooling and heating needs. Factoring these influences supports an effective HVAC design to reduce energy use and operating costs and leads to greater comfort.
Calculating internal heat gains (equipment, lighting, and occupants)
Internal heat gains arise from electrical devices, lighting fixtures and other appliances. The number of occupants and their activities within the building contribute to greater heat production. Precisely calculating internal gains leads to HVAC systems working at the required operating temperatures. Accurately factoring these into the HVAC design process improves energy efficiency and prevents overheating.
Accounting for ventilation and infiltration loads
Infiltration and ventilation loads are crucial for HVAC designers and engineers to ensure the required indoor quality by allowing the introduction of fresh outdoor air. Infiltration takes place through air leaks around windows, doors and walls. These factors affect heating and cooling needs, as external air introduces unwanted heat. Calculating loads in designing an HVAC system that includes maintenance of comfort and efficiency ensures an adequate airflow and greater energy performance.
Tools and software used for HVAC load estimation for efficient HVAC design and installation
Manual J, HAP, and Trace 700 are extensively used tools for HVAC load calculations. Manual J includes standardized guidelines for residential load estimates. HAP, the Hourly Analysis Program (HAP) and Trace 700 are powerful tools utilized for commercial buildings that offer detailed energy analysis and HVAC system design support.
How do these tools improve precision and efficiency?
Tools and software such as Manual J, HAP, and Trace 700 are key for accurate HVAC load calculations. These tools automate complex calculations by incorporating parameters like insulation, building size, and occupancy patterns, which ensure accurate system sizing. Using real-time data and advanced algorithms, HVAC engineers can enhance the efficiency of the design process, lower human error, and enhance energy use. This leads to higher performance, cost savings and faster HVAC installation.
A 3D MEP model for an airport project in the Middle East saves time and costs.
A leading engineering and construction company from the Middle East partnered with HitechDigital for a large airport project. Architectural, Structural, and MEP work was planned for multiple areas of the airport, including passenger terminals, office buildings, and North and South Tier structures. 2D drawings received as input were analyzed and imported into Revit.
While the requirements of the client were straightforward, the team had to navigate various challenges including coordination and collaboration with other trades and identification and resolution of clashes.
Clashes were resolved in Navisworks and a coordinated 3D model MEP at LOD 400 was generated. Accurate quantity takeoffs and coordinated drawings were extracted from the 3D MEP model.
Handing over the deliverables to the client led to:
- Greater time and cost savings for MEPF installation
- Quick completion of the operational terminal
- 100% installation of MEP systems
- Reduction in the number of change orders
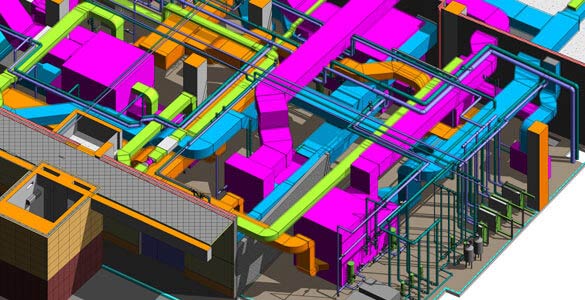 Airport Plantroom MEP System
Airport Plantroom MEP System
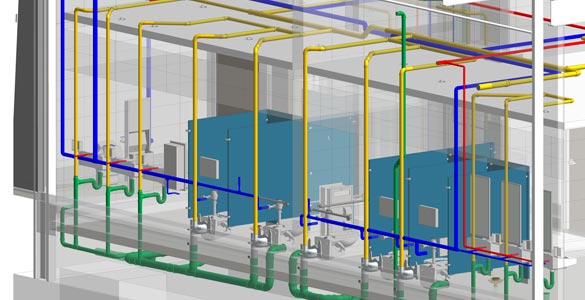 Drainage and Water Supply System
Drainage and Water Supply System
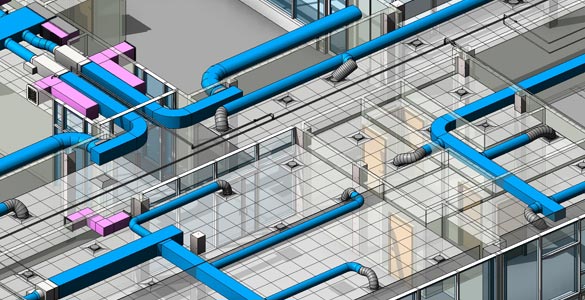 Office Building MEP System
Office Building MEP System
 Under Ground Drainage System
Under Ground Drainage System
Transforming HVAC load calculations for future-ready smart buildings
The future of HVAC load calculations includes the integration of real-time data and IoT sensors to enhance system performance. AI and machine learning will help predict load estimates and improve efficiency. Precise load calculations will also support sustainability, green building and occupant comfort.
Integration with smart building technologies (IoT sensors, real-time data)
The future of HVAC design will depend on the integration of smart building technologies, such as real-time data and IoT sensors. Sensors can track indoor temperature, occupancy, equipment use and humidity. This data is fed into HVAC systems, which enables real-time adjustment to optimize performance. Dynamic adjustment to HVAC systems and current conditions improves energy efficiency, lowers costs, and augments occupant comfort. This ensures a flexible response to evolving requirements.
AI and machine learning for predictive load estimation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will improve HVAC load calculations through predictive load estimation. Using real-time and historical data, these technologies predict heating and cooling needs based on various patterns, such as schedules, occupancy, and weather changes. Predictive analytics will support HVAC engineers in proactively adjusting parameters, reducing energy waste, and preventing under-sizing. With perpetual learning, AI-driven HVAC equipment refines calculations to improve system accuracy and performance. This leads to reduced operational costs.
The role of load calculations in green building certifications (e.g., LEED, WELL)
Accurate HVAC design and installation play a crucial role in garnering green building certifications like WELL and LEED. These certifications focus on sustainability, energy efficiency and occupant health. These parameters are driven by a precise HVAC design. Precise load calculations ensure that HVAC equipment such as air conditioners, heat pumps, furnaces, etc. are correctly sized, reduce energy consumption, and reduce greenhouse emissions. By aligning HVAC system design with green building standards like LEED and WELL, buildings can reduce the environmental impact and ensure comfortable indoor comfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precise HVAC design with accurate HVAC load calculations are key requirements for comfortable, efficient, and cost-effective building systems. By considering parameters such as internal loads, heat gain, and ventilation, HVAC systems can be sized accurately to prevent inefficiencies. HVAC engineers will leverage various technologies, such as predictive analytics, AI, and IoT, to realize precise and dynamic data for improved decision-making.
Furthermore, accurate calculations will simplify compliance with green building standards, which streamline the certification process and promote sustainability. Ultimately, these technologies will improve system performance, lower costs and enhance overall building sustainability.
Need accurate HVAC load calculations for your next project?
Save time and reduce errors in your HVAC designs. Partner with us for precise load calculations.