- Data cleansing fixes errors, removes duplicates, and keeps your data clean and reliable.
- Data enrichment fills in the blanks and brings in extra details to make your data more useful.
- Together, clean, enriched data helps you make better, faster, and more confident decisions.
Table of Contents
- What is data cleansing
- What is the importance of data cleansing
- What are the benefits of data cleansing
- Top 8 data cleansing techniques
- What is data enrichment
- What’s the importance of data enrichment
- What are the benefits of data enrichment
- Top 8 data enrichment techniques
- Data cleansing vs data enrichment
- How often should you clean and enrich your data
- conclusion
Data enrichment and cleansing are two very important yet different processes with the common goal of improving data quality and usefulness. Data cleansing removes errors and redundancies within a dataset, making it accurate and reliable. On the other hand, data enrichment adds new data to the already existing data to improve the information range or fill gaps. The new information added from external sources adds context to the data, adding value.
While data cleansing ensures data accuracy, data enrichment enhances the value and depth of the data. These are complementary processes that work together to enhance data quality and usability. In this blog, we have covered the complexities of data cleansing and data enrichment so that organizations can understand their differences and similarities and can take full advantage of both techniques.
What is data cleansing
Data cleansing is a process that identifies and corrects the data within a dataset to improve data quality. Also known as data cleaning or data scrubbing, this is an important step in preparing data for analysis or decision-making.
There is no single approach that can define the steps of data cleansing because the process varies from dataset to dataset. Very complex data with high errors may require automated algorithms and multi-level verification and validation.
The basic process of data cleansing includes:
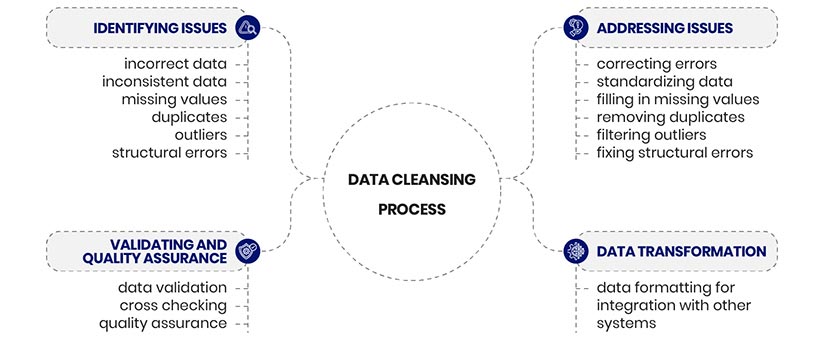
Different tools are used for these multiple processes, which we will discuss a little later in the blog. However, the pace at which the data cleansing tools market is growing globally is a clear indication of the need for data cleansing by organizations. From $3.09 billion in 2024, the market is expected to reach $6.78 billion in 2029.
What is the importance of data cleansing
Even if organizations are extra protective while collecting data there remains a possibility of data getting dirty. Data collected from multiple sources and in different formats has chances of errors creeping in even if you are extra careful.
Dirty data can lead to incorrect beliefs resulting in poor decision making. This can prove especially detrimental in industries like healthcare, finance, and marketing. It can adversely affect operations that rely on clean data for accurate execution.
You create false impressions of your ideal customers and miss out on accurate targeting. This leads to wrong targeting and missed opportunities. And most importantly, you lose your credibility in the market. Imagine sending an email with the wrong name to somebody or with the wrong designation. The person and the organization will not be interested in your campaigns.
To avoid all such negative impacts of dirty data on your business goals it is important to clean your data. Clean data will ensure data reliability and minimize business risks.
What are the benefits of data cleansing
Data cleansing offers various advantages to your business. Accurate and reliable data leads to informed strategies, increases operational efficiency, and reduces the common risk of misinterpretation.
The validation, classification and enrichment of customer profiles in their CRM database enhanced the marketing opportunities of a UK-based organization. The data enrichment process proved beneficial for the organization.
Here are some benefits of data cleansing
- Improved data accuracy and quality – Removes errors, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies, leading to a more reliable and accurate dataset.
- Better decision-making – Allows organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
- Increased productivity – Streamlines data analysis by reducing the time and effort required to prepare the data.
- Reduced costs – Prevents errors and issues from propagating in systems and analytics applications, reducing costs.
- Enhanced customer experience – Clean data, especially in customer relationship management (CRM) systems, leads to more effective marketing and sales efforts.
- Improved compliance – Insures that data meets regulatory requirements and standards, helping organizations avoid penalties and legal issues.
- Increased efficiency – Enables faster decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Reduced storage costs – Removing duplicate or irrelevant data reduces the amount of storage space required, leading to cost savings.
- Improved data consistency – Ensures that data is formatted and organized consistently, making it easier to analyze and interpret.
- Increased revenue – By reducing errors and improving decision-making, data cleaning can lead to increased revenue for businesses.
Fix Bad Data Fast with Proven Cleansing Methods
Learn how data cleansing enhances accuracy and prevents costly mistakes.
Top 8 data cleansing techniques

Data gets dirty very fast. Data cleansing ensures accuracy and consistency of your business data by removing errors and inconsistencies. Key techniques include removing duplicate entries, correcting misspelled names, standardizing address formats, validating phone number structures, filling missing values, filtering outdated records, normalizing inconsistent data formats, and verifying data against authoritative and trusted sources.
These steps are vital when handling data from multiple sources or changing datasets. Regular cleansing maintains data reliability, making it foundational for effective decision-making and further data enhancement processes.
What is data enrichment
Data enrichment is the process of adding new information to an already existing dataset to enhance its usefulness. Mostly, data is added from external sources to enhance data accuracy, completeness, and usefulness. This helps organizations make informed decisions and improve marketing and sales.
For example, with a dataset having just customer names and emails, you can never personalize and target accurately. However, if your data is enriched with their job titles, purchase history, and social media profiles you understand your customers better. Therefore, you can target accurately and get better responses.
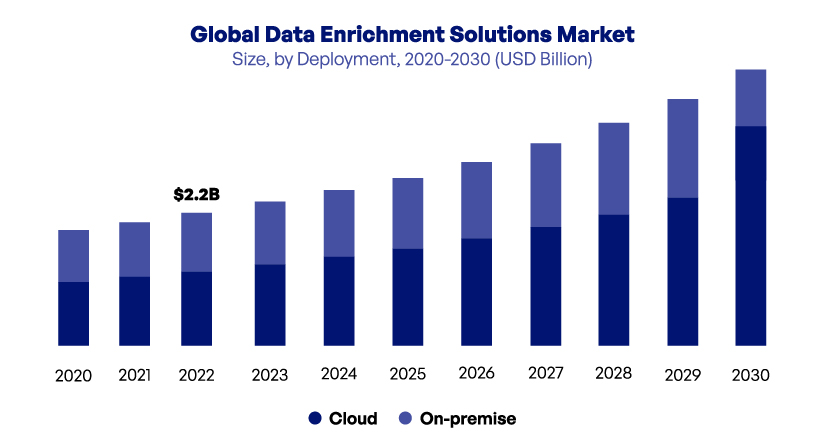
Data enrichment solutions are in great demand as organizations benefit from the enhanced understanding of their customers. The global data enrichment solutions market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2024 to 2030.
Various approaches are used to enhance the value and utility of existing data through new information.
Some of the data that is used to enhance the existing data include
- Demographic enrichment – socio-economic data like age, gender, income, education, and marital status.
- Geographic enrichment – location-based data like postal codes, city, state, and even street addresses.
- Behavioral enrichment – information about customer interactions, such as website activity, purchase history, and engagement levels.
- Technographic enrichment – information about the technologies used by customers or competitors.
- Purchase intent enrichment – browsing history, website interactions, and social media activity.
- App usage enrichment – data about how users interact with mobile apps, this helps optimize app experiences, improve user engagement, and drive app growth.
- Firmographic enrichment – organizational information like company size, industry, and revenue.
- Psychographic enrichment – incorporating lifestyle attributes and preferences to understand customer motivations and values.
What’s the importance of data enrichment
Data enrichment is important for any organization to help gain a comprehensive view of its customers and markets. The raw data often lacks the depth and context needed for effective decision-making.
Data enrichment is a must for every organization as it fills data gaps and helps businesses gain deeper insights. The improved data quality helps with enhanced segmentation and accurate analytics allowing a competitive advantage.
Let us take an illustration to understand the importance of data enrichment. Suppose you have a customer where you have all the details except the name. Shooting an email without the name may not have that impact as when you address the person by name. And this can happen if you enrich your data by adding the name of the person. Further, if you can find the demographic details like age, gender, location, etc. you can target better.
Businesses can use demographic data to segment the audience creating campaigns that align with the group. Moreover, by understanding the preferences of the audience through social media data businesses can anticipate future trends and make strategic decisions about location, expansion, and investment.
Check out how the compilation and enrichment of 500 leads every day enhanced the mailing list performance for a healthcare marketing and advertising company.
Data cleansing and enrichment serve distinct purposes and functions in data management, with complementary processes that help to enhance data quality. Knowing their main differences and intricacies is crucial for efficient data processing and aggregation operations.
What are the benefits of data enrichment
Data enrichment adds context to the data enhancing data quality that offers multiple benefits to the organization. A comprehensive understanding of customers, markets, and trends drives targeted marketing, and personalized customer experience and proves cost-effective. Giving an illustration, the verification of thousands of records with details across 80+ fields and filling up missing details enhanced revenues by winning multiple bids to supply financial data.
Here are some of the top benefits of data enrichment
- Data enrichment reduces inaccuracies, fills gaps, and ensures consistency, making data more reliable for analysis and decision making.
- Enriched data eliminates inconsistencies in formats, ensuring data is standardized and easy to work with.
- Enriching customer profiles with demographic, behavioral, and firmographic data allows for more personalized marketing campaigns and customer experiences.
- Data enrichment provides deeper knowledge of customer preferences, buying behaviors, and overall needs, leading to more effective strategies.
- Enriched data provides a comprehensive view of a business, enabling data-driven decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
- A deeper understanding of customers, markets, and trends derived from enriched data facilitates better strategy development.
- Enriched data can help identify and mitigate risks, such as fraud or default.
- Streamlined processes and automated tasks can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs and save time.
- Data enrichment helps gain deeper insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive actions.
Top – 8 data enrichment techniques

Frequently changing mobile numbers, email IDs, postal codes, designation etc mandate data enrichment. It enhances existing datasets by adding relevant external or internal data to provide more context and depth. Top techniques include appending demographic data, integrating behavioral insights, adding geographic location, tagging customer preferences, enhancing firmographic details, including social media profiles, updating income brackets, and linking industry-specific classifications.
These methods transform clean data into powerful assets, offering deeper customer understanding and improved segmentation. Enrichment is essential when aiming for personalized experiences, targeted marketing, and intelligent business strategies.
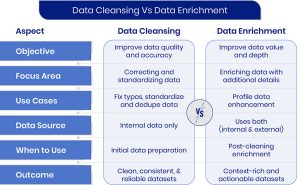
Data cleansing vs data enrichment
Data cleansing and data enrichment are distinct processes with the common goal of improving data quality. Data cleansing removes errors while data enrichment adds new data to the existing dataset adding context to the data.
Data cleansing should be done regularly, especially when dealing with data from multiple sources or when the data is dynamic. On the other hand, data enrichment is done when we need to make the existing data complete and more insightful.
To explain the difference between the two, we can take an illustration. You have a customer database, and you ensure that the data is clean. You would correct misspelled names, correct addresses, remove duplicates, check for the format of phone numbers, and so on. Now that we are sure that the data is clean, we need to make it more insightful. So, next, we start adding industry, customer preferences, income, interests, etc. All this information added through the process of data enrichment will make the data complete and accurate. To thrive in your business, both processes are equally essential.
Both processes are used together to enhance data quality and value.
A US-based client partnered with us to strengthen its 50 million record databases. Using a comprehensive and technology-enabled approach to B2B data sourcing, validation, and enrichment, tailored specifically for a US-based client, we delivered an accurate and updated b2b database.
How often should you clean and enrich your data
Data cleansing and data enrichment are ongoing processes. The frequency may depend on your specific business need or data change rate.
Data enrichment should be planned by everyone on a quarterly or annual basis. You can do it more frequently if the data changes often and for real-time decisions.
But as a rule, data cleansing should be a continuous process, not just a one-time activity, while data enrichment can be performed on a scheduled basis, such as quarterly or yearly.
Considerations for Frequency
- If your data is used for real-time decision-making, you may need to enrich it in near-real time.
- Data decays and becomes unusable, so it’s important to maintain data integrity by cleaning and enriching it regularly.
- The customer lifecycle and its pattern and length indicates how frequently data must be cleaned and enriched.
- Larger datasets may require more frequent cleansing and enrichment.
Regularly assessing your data needs and adjusting your enrichment strategy accordingly is crucial for maintaining data quality and maximizing the value of your information.
Conclusion
Data quality is the key to the success of any industry. Your data must always stay clean and enriched for you to make correct decisions and grow your business. Both processes are equally important. While one keeps your data clean, the other adds context and value to your data. This is a strategic need for your business.
However, both are technical processes requiring constant attention and expertise. You may either develop an in-house team or outsource it to experts. Whatever you decide, one thing is clear; this cannot be ignored. You must get it done regularly.
Go Beyond Cleansing—Start Enriching Data Today
See how enriched data boosts targeting, insights, and decision-making power.






