- Real estate data collection faces challenges like inaccurate and outdated information, access to databases, and integrating various data sources.
- Effective data collection involves gathering information from public records, surveys, and digital platforms, but it is hindered by incomplete records, privacy concerns, and the need for real-time data.
- The field is evolving with advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, requiring adherence to legal standards, continuous data updates, and strong security for data integrity.
In the real estate industry, professionals like realtors, brokers, investors, insurers, and analysts are continually overwhelmed by the task of collecting and analyzing a flood of data. This data ranges from property values and market trends to demographic shifts and comes in staggering volumes, making real estate data collection, and processing a difficult task.
Issues like duplicate entries, incorrect categorization of property listings, or outdated data distort market insights and valuations, leading to missed opportunities and misguided investments. And this weakens customer relations, business performance and revenue.
But in their pursuit to remove all issues from property listing data, real estate stakeholders keep scaling data collection operations, often without putting sufficient checks and balances in place.
The challenges are compounded by dirty data at various sources, and issues with data quality, database access, and integration. And, in a sector where precise and timely data is crucial for success, firms weak on data collection end up with increased headcount and operational costs, revenue losses, and decreased productivity.
Our detailed guide to real estate data collection addresses these hurdles by offering insights and strategies to improve data collection processes and ensure accuracy of property listings. In the next sections we will explore every relevant facet of data collection for the real estate industry, including types, sources, techniques, use cases, validation, legalities, tools, software, and best practices.
Table of Contents
- What is real estate data collection?
- Why does real estate data collection matter?
- What are the key challenges in collecting real estate data?
- Real estate data collection techniques
- Use cases of real estate data collection highlighting real-life examples
- Real estate data quality, validation, processing, and analysis
- Privacy and legal considerations
- Tools and software for real estate data collection
- Effective real estate data collection best practices
- The future of real estate data collection
What is real estate data collection?
Real estate data collection refers to the process of collecting and analyzing relevant information about properties from various sources in order to make better decisions about buying, selling, renting, or investing in properties. Various property details include shades of information such as size, location, and ownership, but also history about past sales prices, renovations, neighborhood information, and demographic information. With enough information a real estate professional can paint an accurate picture of the market trends over time and property value.
In today’s digital world, data collection has evolved since the days in which we relied on property records and hand-written surveys. With the advent of online listings present on platforms you can now collect data through your computer. Additionally, multiple listing services (MLS), geographic information systems (GIS), drone imaging, and AI algorithms and tools have all changed the way we collect data, and provided us with a much shorter tool-case, between the time we collect, analyze, and report the results. With these advances, the amount of data that can be collected is immeasurable and can be observed in real time.
For companies, developers, and investors, data collection and analysis are the first step in creating a plan. It is often the base for determining risk analysis, tracking market behavior, and watching market trends and consumer preferences. For a residential property, commercial property, or a multi-development property, the data will show the information needed to base decisions around facts rather than on assumptions.
Why does real estate data collection matter?
Real estate is a high-value industry where even small mistakes even minor mistakes can lead to costly outcomes. If data collection is accurate then uncertainty can be reduced by understanding property values, demand trends, leasing yields and level of competition. This allows in all stakeholders the ability to make good decisions to match various financial objectives.
For property developers, it is important to collect data as it allows them to find the best locations, assess construction viability, and assess future demand. In terms of investment, it uncovers the ROI on property, identifies developing markets while mitigating risks associated with the real estate cycle. In the case of real estate agents, it increases their ability to match their buyers with the appropriate property while providing evidence-based information.
Additionally, data collection in the real estate market creates the ability to adapt at a rapid pace to a market because consumer behavior can change without notice and our economy can be unreliable. Data collection can highlight demand in properties before the competition, allow real estate professionals to track regulatory legislation more easily, and allow customization of client experiences.
What are the key challenges in collecting real estate data?
Data collection in real estate is the systematic gathering of information about properties, markets, transactions, and related factors from various channels, such as real estate public records, surveys, and digital platforms. Property data collection aids in the analyses that form the foundation of decisions in property valuation, market analysis, and investment strategies.
However, the sheer volume and diversity of data, coupled with the legal implications of data access, collection, and use, brings multiple challenges in real estate data collection.
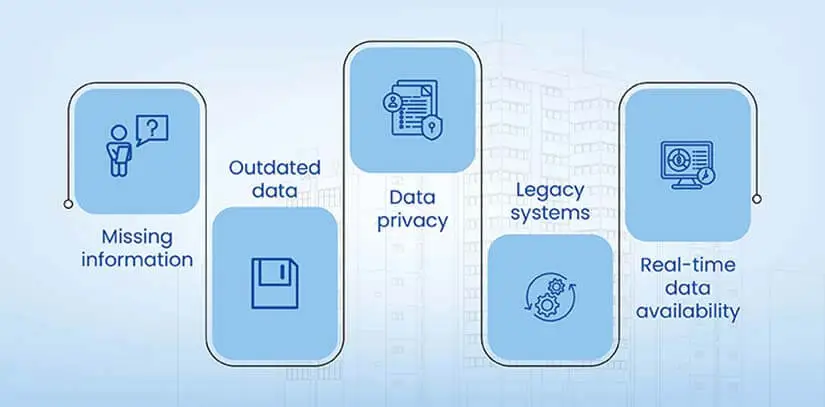
- Incomplete or inaccurate public records: In publicly available property records, for missing data elements, records will be incomplete, while some data elements will have incorrect values. These discrepancies will raise the requirement to fill the gaps.
- Data privacy concerns: Lack of a requisite data privacy framework or non-adherence to standards can jeopardize the security of sensitive personal or financial data. Due attention needs to be given to strike a balance between data usage and data privacy.
- Technological limitations: Sticking to outdated systems or limited technological adoption can collapse the data collection project by creating constraints in the process.
- Ascertaining data accuracy: Ensuring the precision and reliability of real estate data is a challenge due to potential discrepancies in public records, outdated information, and the dynamic nature of property details.
- Assuring real-time data availability: Obtaining up-to-the-minute real estate information is a challenge, as the market is constantly changing, with property statuses, prices, and availability fluctuating rapidly.
- Ascertaining authenticity of data: Verifying the authenticity of real estate data is crucial, as inaccuracies or fraudulent information can lead to costly mistakes.
- Validating structure of data at different data sources: Integrating data from various sources in real estate can be complicated by differences in formats, terminologies, and data structures.
- Lack of standardization: Real estate data may come from various sources and may not follow standardized formats or terminology, making it difficult to aggregate and analyze.
- Fragmented nature of data: Property data is spread across various government agencies, private databases, and online platforms, making it challenging to consolidate and cross-reference.
- Anomalies brought about by property condition changes: Properties can undergo renovations, damage, or other changes that may not be immediately reflected in public records.
- Zoning and land use changes: Changes in zoning regulations or land-use designations may not be promptly updated in public records, leading to potential discrepancies.
- Data integration challenges: Integrating data from various sources, such as MLS listings, county records, and private databases, can be technically challenging and may require custom solutions.
Real Estate Data Collection Techniques
| Data Collection Technique | What is It? | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Data Collection | What is It? Physically collecting data through on-site visits, interviews, and observations. | Implementation Example Visiting properties to document their condition, features, and surroundings or making direct observations of properties and their surroundings. |
| Automated Data Scraping | What is It? Using software and scripts to extract data from websites and databases in an automated fashion. | Implementation Example Using APIs to automatically retrieve data from real estate databases or employing data scraping tools to collect market data on property prices and trends. |
| Surveys and Interviews | What is It? Directly gathering information from property owners, residents, or stakeholders through structured interviews or surveys. | Implementation Example Conducting structured interviews with residents to understand their experiences and preferences related to the property. |
| Geospatial Technology for Mapping | What is It? Using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and mapping tools for the collection of spatial data and visualizing property information. | Implementation Example Using satellite imagery to analyze terrain and land features for potential development or investment. |
| Utilizing Multiple Listing Service | What is It? Accessing a centralized platform where real estate professionals share and access comprehensive property listings. | Implementation Example Real estate agents use an MLS platform to list and search for properties on behalf of their clients. |
| Use of Data Collectors in Appraisal Processes | What is It? Employing specialized tools and methodologies to gather and analyze property data for the valuation of real estate assets. | Implementation Example Using data collectors to measure and document specific property attributes such as square footage, room counts, and condition. |
Use Cases of Real Estate Data Collection Highlighting Real-life Examples
The rise in MLS listings, property management platforms, and tech-awareness among real estate companies has led to a higher use of machine-learning techniques or rule-based methods for gathering and analyzing real estate data.
Here are some ways in which companies operating in the real estate spectrum are collecting data for data-driven decisions:
House buyer sentiment analysis
Zillow leverages data to analyze consumer preferences, sale trends, and stakeholder feedback to understand all the practical and emotional factors that influence buying decisions. It uses elements such as the number of rooms, property type, pricing, and location to optimize marketing and advertising tactics.
Property market analysis
This analysis is a common exercise for MLS listings, such as Realtor and Redfin. They analyze data such as property values, demand trends, and economic indicators to identify current project expansions, mortgages, insurance, and loan ranges.
Price optimization
MLS sites use data to determine the most competitive and profitable listing price for a property. They gather data on various market variables, property features, and demand-supply dynamics to analyze pricing ranges by the dimension of the property, pricing type (sale, mortgage, or rent), and location.
Tenant onboarding
Property management software platforms such as Cozy and Buildium use data to streamline the process of welcoming new tenants. They gather data on elements such as rental history, tenant preferences, and credit scores to automate the tenant screening process so that they experience a smooth onboarding experience.
Real Estate Data Quality, Validation, Processing, and Analysis
Accurate and reliable data forms the foundation of informed decision-making in every industry, especially real-estate. These measures are essential for ensuring data integrity and preventing costly errors in property valuations, market analysis, and investment strategies.
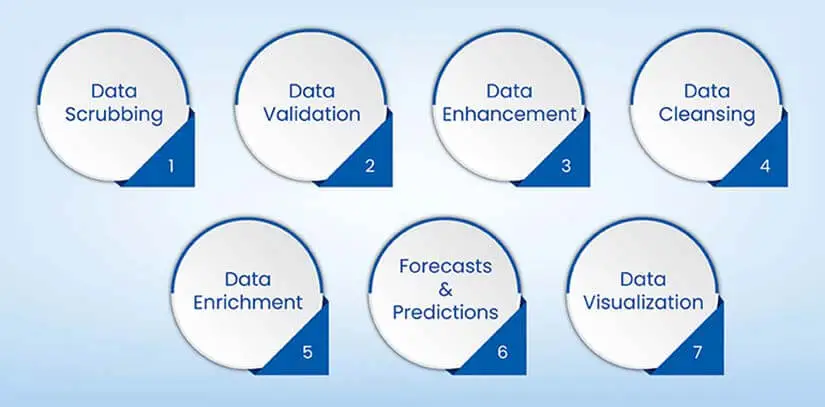
To ascertain data quality, the following process must be implemented:
Cleaning and scrubbing
Cleaning meticulously reviews and rectifies real estate data, targeting errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies.
Verification and validation processes
These steps ensure that real estate data is trustworthy and accurate. By cross-referencing multiple reputable sources, any discrepancies or inaccuracies can be identified and corrected.
Dealing with missing or inaccurate data
When faced with incomplete or inaccurate data points, it’s important to have effective strategies in place. Here, you need to implement techniques such as data imputation or seek additional reliable sources to fill in the gaps.
Data cleaning and preprocessing
This removes inconsistencies and errors from collected data, ensuring it is accurate and ready for analysis.
Data enrichment
This enhances raw data with additional information or attributes, providing a more comprehensive view for analysis. It is a key step before training a model on data.
Predictive modeling
Employs statistical algorithms to make informed forecasts and predictions about real estate trends, prices, or market behavior.
Data visualization
Uses graphical representations to present real estate data, making complex information more accessible and understandable for stakeholders.

How to leverage online Clustering Algorithms and APIs to tackle fluctuating volumes in real estate data aggregation
- MLS APIs and web scraping together enhance the accuracy of real estate listings.
- Clustering APIs provide direct access to MLS data, web scraping captures additional information.
- The combination ensures comprehensive, current property details, improving data quality.
Privacy and Legal Considerations
The sensitive nature of real estate makes its handlers tremendously responsible for ascertaining its safety at each touchpoint. As stated, legalities in real estate data processing demand equal attention to the process of collection. As a result, those dealing with and using real estate must adhere to the regulations, instructions, and practices discussed below.
GDPR and real estate data
Mandates strict guidelines for handling personal data in real estate. It requires obtaining clear consent and providing individuals with control over their information.
Compliance with local regulations
Adhering to specific regional or national laws governing real estate data privacy is paramount. It is a mark of how data collection practices align with legal requirements, safeguard the privacy rights of individuals, and maintain trust within the industry.
Ethical data handling practices
Real estate professionals have an ethical obligation to handle data responsibly. They must obtain consent and use data solely for legitimate purposes.
Attribution and fair use
When utilizing data obtained through web scraping, give proper credit to the source or MLS provider. It is important to have a transparent process and demonstrate respect for the original data creators.
Respect copyright and intellectual property
Respect intellectual property rights, copyright laws, and fair-use principles. Distinguish between your content and data sourced from MLS APIs or web scraping in your listings or publications.
Understand and comply with terms of service
Before beginning real estate data collection, ensure that your use of MLS APIs and web scraping aligns with the policies and guidelines of the MLS provider or any website you plan to scrape.
Obtain proper authorization and permissions
It is important to demonstrate respect for data ownership and legal compliance to reduce the risk of unauthorized data usage. So, always obtain explicit authorization and permissions from MLS providers, website owners, or relevant authorities before accessing or scraping their data.
Monitor legal and ethical considerations
Stay informed about the legal and ethical considerations surrounding web scraping, data usage, and MLS APIs. Regularly review, update and align your practices with growing legal data standards.
Tools and Software for Real Estate Data Collection
| Tool/Software | Implementation Example |
|---|---|
| Tool/Software Data Scraping Tools | What it Does Software and tools designed for extracting data from websites and databases, automating the process of data collection. Examples include Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Octoparse. |
| Tool/Software GIS and Mapping Software | What it Does Platforms like ArcGIS, Google Earth, and QGIS that enable the visualization of spatial data, including property boundaries, land use, and geographical features. |
| Tool/Software Survey and Questionnaire Platforms | What it Does Tools for creating and conducting surveys to collect structured data from respondents. Some such tools include SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, and Typeform. |
| Tool/Software MLS (Multiple Listing Service) | What it Does A centralized database used by real estate professionals to share and access comprehensive property listings, enhancing market transparency and exposure. |
| Tool/Software Aerial Imagery Platforms | What it Does Services like Nearmap or Google Earth that offer high-resolution aerial imagery for analyzing properties and their surroundings. |
| Tool/Software Real Estate CRM Systems | What it Does Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems tailored for real estate professionals, often containing tools for managing leads, contacts, and property data. |
| Tool/Software Real Estate Investment Software | What it Does Tools like REFM or ARGUS for financial modeling and analysis of real estate investments, including property valuation, cash flow projections, and ROI calculations. |
Do not compromise on the quality and integrity of your real estate data.
Choose accuracy, precision, and unmatched reliability.
Effective Real Estate Data Collection Best Practices
Successful real estate data collection can be realized only by following best practices, as it will prevent loss of time and cost in collecting non-useful data. Follow these best practices for a successful data collection process.
Establish clear objectives
Define the goals to guide the data collection process. With targets set right, the gathering of information will be aligned with specific purposes, whether it’s market analysis, property valuation, or investment decisions.
Regularly update and maintain data
Keeping data current and accurate will reduce your reliance on obsolete information. As a result, professionals will be able to make informed decisions based on the most recent market trends and property details.
Cross-verification with multiple sources
Validating data through cross-referencing ensures its accuracy and reliability. Relying on multiple trusted sources reduces the risk of relying on potentially flawed or incomplete information.
Data security measures
We have already seen the importance of the security and privacy of real estate data. So, you need to implement robust security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential legal consequences while maintaining trust and compliance.
Monitor changes and adapt
Regularly monitor MLS APIs and websites for any changes in their data structures, formats, or terms of service. Adapt your scraping methods accordingly for continued accuracy and reliability.
The Future of Real Estate Data Collection
Real estate data collection has evolved from being a manual exercise to becoming a tech-driven and automated process. It is expected to grow in line with the following trends.
Advanced analytics and AI
The real estate sector is poised to make increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics for more sophisticated insights and predictions regarding real estate trends, pricing, and market behavior.
IoT and smart buildings
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices will prove instrumental for collecting real-time data on building performance, energy usage, and tenant behavior.
Blockchain-based property tokens
Tokenization platforms can allow fractional ownership of real estate assets through blockchains, enabling more accessible and liquid investment opportunities.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Use of VR and AR for virtual property tours is emerging rapidly. It can be a potential source of data on interior features and layouts.
Predictive analytics for property valuation
In real estate, predictive analytics needs special mention. Every type of business in the industry is keen on making advancements in its predictive capabilities using machine learning.
Geospatial data for site selection
While geospatial data for location intelligence is already in regular use, it will reach a more accurate and detailed form soon.
Environmental and sustainability data
Sustainability is a key area affecting every sphere and is especially important to real estate. Going ahead, most businesses in the field will incorporate environmental impact and sustainability data into property evaluations.
Conclusion
For stakeholders in the real estate industry, navigating the complexities of the industry requires a strategic and thorough approach. Success hinges on the effective collection, analysis, and application of varied and comprehensive datasets. This involves leveraging advanced technology to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Adherence to legal and ethical standards is not just a requirement but a cornerstone of responsible data management. The essence of effective data aggregation lies in maintaining up-to-date and precise information, which in turn enables insightful market analysis and informed decision-making.
By remaining adaptable and well-versed in evolving market trends, real estate firms and their data aggregators can transform their data into a powerful tool, guiding strategic initiatives and shaping informed decisions in the real estate sector. This focused and flexible approach in data collection is crucial for staying ahead in the competitive world of real estate.
Maximize opportunities with data-driven property insights.
Harness the power of robust real estate data collection services.







