- Factors like demand fluctuations, miscommunication, and lead time variability affect optimal resource usage and creates roadblocks in production planning and scheduling.
- Tools like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) leverages real-time data to improve communication between planning and execution phases.
- MES focuses on automated and logic-driven planning and scheduling methods to stay flexible for changes in master schedule, optimize resource usage and implement strict quality control.
Efficient production planning and scheduling are critical for custom job shops like millworkers and sheet metal fabricators, specializing in high variety but small volumes of work. A robust plan and schedule ensure higher production throughput and quality with optimal resource usage.
Today, there are tons of tools and software platforms available for the planning and scheduling of jobs. These tools use logic-and constraints-backed algorithm, and account for customer and order priority for planning. This comprehensive guide explores production planning and scheduling module of an MES software to fit the unique needs of your industry.
MES bridges the gap between planning and execution, offering real-time data, enhancing communication, and boosting overall efficiency. The Production Planning and Scheduling module of a powerful Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is not just helpful—it’s essential. It’s the technological glue that holds the complex processes of production planning and scheduling together, ensuring that your operations run like a well-oiled machine.
By integrating advanced production planning and scheduling software with other business enterprise systems, companies can bypass traditional barriers, achieving exceptional levels of productivity and precision.
Table of Contents
- Challenges in Production Planning and Scheduling
- Benefits of having a robust plan and schedule for production
- Methods for Production Planning and Scheduling: Traditional VS Digital
- Production Planning Strategies with MES
- Features of MES to Optimize Scheduling
- Benefits of MES in Production Planning and Scheduling
- Key Features of MES for Production Planning
- Implementing MES in Small and Medium-Sized Plants
- Measuring the Impact of the MES You Choose to Implement
- Future Trends in MES and Production Planning & Scheduling
Challenges in Production Planning and Scheduling
Understanding the challenges of effective production planning and scheduling, particularly in a job shop setting is crucial. In a small sized manufacturing floor, each issue can significantly impact operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Here are some common issues and their impacts:
1. Unbalanced production due to demand fluctuations
Demand fluctuations refer to the variability in customer orders. This can be due to seasonal trends, market volatility, or changing consumer preferences.
Impact on Job Shop: In a job shop, production levels are mainly -order driven. So, in the case of higher-than-expected demand, shops face capacity issues. Alternatively, if the demand dips, resources remain idle. On top of this, as inventory is often specialized, lead time and delivery become major concerns for manufacturers. This makes resource planning more complex.
2. Miscommunication due to siloed systems (Sales order, documents, scheduling, shop floor tracking, etc.)
Siloed systems mean a lack of integration and communication between different software systems, departments, and workstations for smooth production management.
Impact on Job Shop: Failing to meet customer requirements can cause lost business, a negative reputation, and reduced customer loyalty. It can also lead to increased costs due to reworking or expedited shipping to meet deadlines. For job shops, which often deal with highly customized orders, this challenge is acute.
3. Lead time variability due to operational inter-dependencies
Delays in the supply chain or production process can cascade down the line, causing delays and inefficiencies throughout the production cycle.
Impact on Job Shop: Variability in lead times for raw materials, components, and parts can disrupt production schedules and impact overall efficiency. The impact of lead-time variability due to operational inter-dependencies in job shops includes production delays, resource inefficiencies, and challenges in inventory management.
Benefits of having a robust plan and schedule for production
- Efficient Resource Allocation: A detailed plan and schedule enable businesses to allocate resources such as manpower, materials, and equipment more efficiently. This prevents over-allocation or underutilization of resources, optimizing costs, and maximizing productivity.
- Minimized Downtime: With a well-defined schedule, downtime can be minimized as workflows are streamlined and potential bottlenecks are identified and addressed proactively. This ensures continuous operation and reduces the risk of delays or disruptions in production.
- Improved Quality Control: A structured plan allows for better monitoring and control of the production process. By adhering to a predefined schedule, organizations can implement quality control measures at each stage, ensuring that products meet or exceed standards consistently.
- Enhanced Time Management: A robust schedule helps manage time effectively by prioritizing tasks and setting realistic deadlines. This fosters a culture of accountability and encourages employees to adhere to timelines, boosting overall productivity.
- Optimized Inventory Management: A well-planned production schedule facilitates better inventory management by aligning production with demand forecasts. This prevents overstocking or stockouts, reduces carrying costs, and minimizes the risk of obsolete inventory.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Consistent delivery of high-quality products within the stipulated timeframe enhances customer satisfaction. A reliable production schedule ensures timely order fulfillment, reduces lead times and builds trust and loyalty among customers.
- Risk Mitigation: A comprehensive plan accounts for potential risks and contingencies, allowing organizations to proactively mitigate them. By identifying potential challenges in advance, businesses can implement measures to minimize their impact on production timelines and overall operations.
- Facilitates Continuous Improvement: A structured production plan provides a basis for performance evaluation and continuous improvement initiatives. By analyzing production data and feedback, businesses can identify areas for optimization and implement changes to enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
- Cost Savings: Overall, having a robust plan and schedule for production leads to cost savings across various aspects of operations. From reduced overtime expenses to lower inventory carrying costs and improved resource utilization, businesses can achieve significant cost efficiencies by implementing an effective production schedule.
Methods for Production Planning and Scheduling: Traditional VS Digital

Traditionally, schedulers and production managers have dealt with production planning and scheduling processes through manual and paper-based systems. These methods are familiar to schedulers but also present several limitations. With the advent of digital technology, most of these limitations have been overcome. A production planning and scheduling software offers automation, accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility in the planning process.
Challenges of Traditional Methods for Production Planning and Scheduling
Traditional production planning and scheduling methods often suffer from a lack of real-time visibility and an inability to adapt quickly to changes. This rigidity can lead to inefficiencies, such as production delays, increased downtime, and the underutilization of resources. The reliance on human judgment and experience, while valuable, can also introduce errors and inconsistencies in planning.
Paper-based systems are characterized by their physical production plans and schedules, often documented in spreadsheets or charts. These systems are inherently static, making it difficult to update and share information in real time. This delay in information flow can lead to a lack of coordination among different departments, affecting overall production efficiency.
Difficulties with Manual Data Entry and Record Keeping
Typically, with Excel spreadsheets, we have manual data entries. It is not only time consuming but also prone to errors, leading to inaccuracies in inventory levels, production schedules, and overall operational planning. These inaccuracies can have a cascading effect, resulting in cost overruns and missed deadlines.
Risks of Decision Making with Physical Planning Boards
Physical planning boards, while providing a visual representation of schedules, are limited in their ability to handle complex scheduling scenarios. They require manual updating, which is not only labor-intensive but also increases the risk of outdated or incorrect information being used for decision making.
Siloed and Delayed Communication
Traditional methods often rely on face-to-face meetings, phone calls and emails for communication. This can lead to information silos and delays in communication, impacting situations requiring quick decision-making or adjustments to production schedules.
Sluggish Scheduling and Adjustments
In traditional settings, scheduling and making adjustments can be a cumbersome process, often requiring the reworking of entire schedules. This inflexibility can lead to inefficiencies, especially in responding to unexpected changes or customer demands.
Inventory Management Hassles
Traditional inventory management often struggles with maintaining the right balance of stock. Without real-time data, it’s challenging to optimize inventory levels, leading to either excess stock, which ties up capital, or stock-outs, which can halt production.

Implementing an MES for job shop owners
- Do you still manually plan production?
- Can you track and trace all manufacturing orders?
- How updated are your reports on machine availability?
- Ask many more questions like this to assess your job shop’s maturity.
Benefits of Using Digital Methods for Production Planning and Scheduling
In contrast, digital methods using project management applications, MES, or ERP systems offer several advantages. They provide real-time visibility of all aspects of production, enabling more accurate and efficient planning. Automated data collection reduces errors associated with manual entry, while advanced analytics helps in making more informed decisions. Digital systems facilitate better communication and collaboration, allowing for quick adjustments and more agile responses to changing demands. Additionally, digital inventory management is more precise, reducing the risks of overstocking or stock-outs, thus optimizing resource utilization.
Production Planning Strategies with MES
MES offers logic-driven production planning and scheduling solutions to develop master schedules that transform the way manufacturing orders are processed. The algorithms use data from the shop floor to develop schedules and plans. This data includes resource availability, customer priority, committed timelines, and skill requirements.
MES facilitates leveraging the Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing approach, applies the Theory of Constraints (TOC), and lean manufacturing principles to significantly reduce waste. Let’s look into each of these and what the functionalities of MES are that help in implementing these approaches.
Master the art of optimally planning and scheduling manufacturing orders.
Read along for insightful tips and strategies to elevate your production planning with MES.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Manufacturing with MES

For custom millworkers and metal fabricators, the Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing approach helps them operate economically. By providing real-time data and analytics, MES enables manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimize inventory levels, enhance production process quality, and minimize waste. This system ensures that materials and components are only ordered and produced as per demand, reducing the costs associated with excess inventory.
Key functionalities of MES that support JIT
MES tracks inventory in real time by integrating with shop floor operations, using barcode/RFID scanning for instant updates. It also communicates with ERP systems for accuracy, monitoring work-in-progress, enabling demand-driven replenishment.
It supports JIT manufacturing by ensuring materials are ordered and restocked based on actual production needs. It also reduces excess inventory and ensures materials are available precisely when needed. This brings down overall waste and enhances production efficiency.
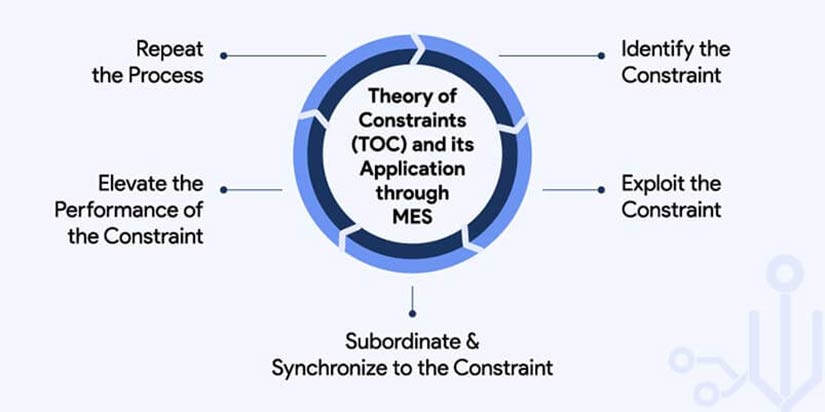
The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is applied in MES by identifying and managing bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. MES tracks production flow in real time, highlighting constraints such as long queue times, identifying root cause, etc. that limit throughput. By focusing on these constraints, MES enables targeted improvements, optimizing production efficiency, and increasing output in line with TOC principles.
Key functionalities of MES that support the application of TOC include:
- Bottleneck Identification: MES monitors key machine parameters such as performance, job processing time, machine utilization, etc. and sends alerts on deviations from expected throughput. This insight allows manufacturers to focus on alleviating these constraints to improve overall throughput.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: MES identifies and analyzes production bottlenecks, enabling targeted actions to optimize throughput, reduce cycle times, and improve overall process efficiency. This aligns with TOC’s focus on systematically improving the constraint until it’s no longer the limiting factor in production.
- Performance Measurement: MES tracks the performance of various processes, and highlights anomalies. This helps the workstation manager measure the impact of changes that need to be made to ease constraints and optimize production flow.
Lean Manufacturing and Waste Reduction with MES
Lean manufacturing is all about doing more with less, and MES is the cornerstone technology in achieving this. In the context of millwork and sheet metal fabrication, where there are multiple types of products being manufactured, precision and efficiency take the center stage.
Key functionalities of MES that support reducing waste significantly:
- Optimal Resource Utilization: MES uses logical algorithms with preset templates that can be customized to allocate job orders to various machines. It also accounts for optimum use of resources, including labor and materials, by integration with other platforms like HRMS and WMS for effective planning.
- Process Optimization: MES provides user-based dashboards and reports to give detailed insights into every production stage. This allows for the identification and elimination of machine-wise inefficiencies that lead to waste.
- Quality Control: Enhanced quality control capabilities of MES ensure that defects are identified and rectified promptly, reducing material waste and rework.
Features of MES to Optimize Scheduling
MES’s algorithm-based scheduling, workload balancing capabilities, and adept handling of disruptions and changeovers make it an indispensable part of modern manufacturing operations.
Algorithm-Based Scheduling for Efficiency
MES leverages advanced algorithms that consider factors, such as machine availability, labor, skills, material requirements, and delivery deadlines to streamline the scheduling process. By doing so, MES can:
- Prioritize Orders: MES can prioritize orders based on criteria like due date, customer importance, or the complexity of the job. It can assign orders to machines and assembly lines based on these criteria so that there is no negative effect on production.
- Optimize Production Flow: By analyzing production sequences, MES identifies the most efficient production paths. This approach enables minimizing changeover times and enhancing throughput across production lines.
- Maximize Resource Utilization: MES algorithms ensure that machines and labor are used to their fullest potential, reducing idle time. It offers auto-routing of assemblies across the shop floor for minimum movement and optimal resource utilization.
Handling Unexpected Disruptions and Changeovers
MES’s capabilities in rapidly responding to unforeseen events, minimizing downtime during changeovers, and fostering continuous improvement are indispensable in manufacturing environments.
- Rapid Response to Disruptions: When custom manufacturing shops face machine breakdowns, material shortages, or last-minute orders, MES provides the agility to recalibrate production schedules with minimal disruption. By swiftly reorganizing resources and priorities, MES helps maintain a steady flow of operations, even in the face of unexpected challenges.
- Minimizing Downtime During Changeovers: Changeovers can be a significant source of downtime in manufacturing. MES analyzes various factors, such as machine setup times, workforce availability, and material requirements, and orchestrates a changeover that minimizes downtime. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining high productivity levels and meeting tight production schedules.
- Continuous Improvement: One of the most significant advantages of MES is to offer real-time insights to evaluate the root causes of inefficiencies and delays. By understanding these factors, manufacturers can develop strategies to prevent future disruptions and refine manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and higher quality outputs.
Benefits of MES in Production Planning and Scheduling
MES brings a suite of benefits that are impactful for millworkers and sheet metal fabricators for timely delivery. Some of these benefits include:
-
Improved efficiency and productivity
By integrating MES, these industries witness a significant improvement in efficiency and productivity. The system streamlines processes, minimizes manual data entry, and reduces errors, leading to a more efficient production line. This efficiency is critical in custom millwork and precision metal fabrication, where each project has unique specifications and tight deadlines. MES enables faster turnaround times and higher throughput, ensuring that customer demands are met promptly and accurately.
-
Enhanced supply chain management
MES plays a pivotal role in enhancing supply chain management. Due to availability of different grades wood, metals, and finishing materials, managing the supply chain effectively is vital. MES provides detailed tracking and monitoring of materials, from procurement to usage, ensuring optimal inventory levels and reducing waste. This level of control is essential for maintaining cost-effectiveness and meeting project timelines.
-
Optimized shop floor operations
For custom manufacturing processes, MES optimizes and ensures efficient usage of machinery, timely maintenance, and smooth workflows. This optimization leads to a reduction in machine downtime, improved safety, and a more organized and productive work environment.
Experience unparalleled efficiency, agility, and quality in your production processes.
See how Hitech i2i – our production planning software solution can streamline your production
Key Features of MES for Production Planning
In the millwork and metal fabrication industry, the adoption of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) provides access to a robust set of features that bolster production planning. These features are indispensable for precision, efficiency, and competitiveness.
-
Real-time Data Collection and Analysis
Beyond just collecting data, MES systems offer real-time data analysis. This feature provides actionable insights by identifying trends, potential bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. For millwork and metal fabrication, this means the ability to proactively address production challenges and continuously refine processes.
-
Automated Scheduling and Resource Allocation
MES automates scheduling and resource allocation, ensuring that materials, equipment, and labor are optimally used. This feature helps to meet project deadlines and reduce operational costs.
-
Quality Management and Compliance Tracking
MES incorporates robust quality management tools that help monitor and maintain high-quality standards. It also ensures compliance tracking, which is crucial in industries with strict regulations and standards.
-
Customizable Dashboards and Reporting Tools
The flexibility of customizable dashboards and reporting tools in MES allows businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs. This feature empowers decision-makers with relevant, real-time information to make informed choices.
-
Integration with ERP Systems
Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems is a key feature of MES, as it ensures seamless data flow and coordination between production planning and other aspects of a business, such as finance, procurement, and inventory management.
-
Visual Layout of Production Schedules
MES offers visual representation of production schedules, making it easier for teams to understand and coordinate tasks, reducing the likelihood of errors and miscommunication.
-
Quick Read Process Monitoring Capabilities
MES provides quick-read process monitoring capabilities, giving operators and managers instant access to critical data without navigating complex systems.
-
Automated Sequence Planning
This feature automates the sequencing of manufacturing orders and processes using logic-and constraints-based algorithms. It ensures optimizing production schedules and reducing the time needed to plan and execute projects.
Thus, MES empowers job shop owners to meet the unique demands of these sectors, maintain high-quality standards, and thrive in a dynamic market.
Implementing MES in Small and Medium-Sized Plants
Implementing MES in small and medium-sized plants streamlines operations, enhances efficiency, and improves data-driven decision-making. It optimizes production processes and ensures competitiveness in a rapidly changing manufacturing landscape.
The implementation process can involve several steps depending upon the MES partner you have. Here are the sequential steps involved.
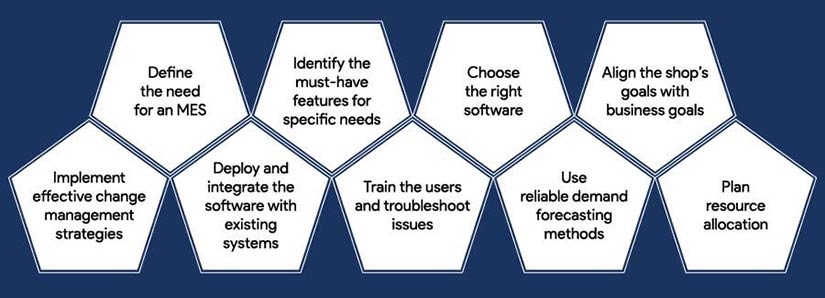
Measuring the Impact of the MES You Choose to Implement
Measuring the impact of MES involves assessing various aspects of manufacturing operations before and after MES implementation. MES systems improve manufacturing efficiency, quality, and compliance by tracking and documenting the transformation of raw materials to finished goods. Here are key aspects to measure its impact:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
By focusing on the key metrics from the shop floor data, you can predict the impact of implementing MES.
- Cycle Time Reduction: Measure the time taken for a product to move through the entire production process. A decrease in cycle time post-MES implementation indicates improved efficiency.
- Quality Improvements: Assess the impact on product quality by measuring the rate of defects, rework, and returns. A decrease in these metrics indicates an improvement in quality control.
- Equipment Efficiency: This is a primary metric for evaluating manufacturing productivity. OEE measures the effectiveness of manufacturing equipment by combining availability, performance, and quality metrics.
- Inventory Turnover: MES leads to better inventory management. Compare inventory levels, turnover rates, and carrying costs before and after MES implementation.
Long-term Benefits of MES Implementation
There are some long-term benefits of implementing MES impacting the efficiency of your plant and they show returns on your investment in the technology. Some of these include:
- Enhanced Operational Visibility: MES provides a comprehensive view of the production floor, enabling better decision-making and process optimization.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As your millwork or metal fabrication business grows, MES can adapt and scale, supporting increased complexity and volume.
- Workforce Empowerment: MES tools empower employees with information and analytics, leading to improved productivity and job satisfaction.
- Sustainable Practices: By optimizing resource usage and reducing waste, MES contributes to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Continuous Improvement: MES facilitates a culture of continuous improvement by providing data-driven insights for ongoing process enhancements.
ROI Analysis
- Cost Savings: Analyze how MES reduces operational costs through efficient resource utilization, waste reduction, and energy savings.
- Revenue Growth: Evaluate case studies in which MES implementation has led to increased production capacity and revenue growth.
- Investment Payback Period: Highlight examples showing the typical payback period for MES investments in the millwork and metal fabrication sectors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Include case studies demonstrating improved customer satisfaction due to better quality control and timely deliveries.
- Competitive Advantage: Discuss how MES integration has given companies a competitive edge in the market.
By focusing on these aspects, manufacturers can make informed decisions about implementing the right MES and leverage its full potential for improved production planning and scheduling.
Future Trends in MES and Production Planning & Scheduling
The future of MES and production planning is marked by integrating Industry 4.0 technologies, AI and machine learning-driven optimization, and a strong emphasis on sustainability.
1. The Rise of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factories
The future of MES and production planning is closely tied to the ongoing evolution of Industry 4.0 and the emergence of smart factories. Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, characterized integrating digital technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT), and automation into manufacturing processes. MES plays a pivotal role in this transformation by connecting the shop floor with the digital world.
- Digital Twin Technology: MES will increasingly incorporate digital twin technology, allowing manufacturers to create virtual replicas of physical production systems. These digital twins enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and simulations for process optimization.
- IoT-Driven Connectivity: MES will leverage IoT sensors and devices to collect vast amounts of data from machines, equipment, and products. This data will be used for real-time decision-making, quality control, and remote monitoring of production lines.
- Advanced Analytics: MES systems will adopt advanced analytics to provide actionable insights from the data collected. Predictive analytics will enable proactive maintenance and optimization of production schedules, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
2. AI and Machine Learning in Production Planning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into MES and production planning will revolutionize how manufacturers optimize their operations. These technologies will enhance decision-making, automate routine tasks, and improve overall efficiency.
- Predictive Production Planning: AI-driven algorithms will analyze historical production data, demand forecasts, and supply chain information to generate highly accurate production schedules. This will minimize overproduction, reduce lead times, and optimize resource allocation.
- Quality Control: AI-powered image recognition and machine learning models will be used for real-time quality control. Defects can be identified and addressed immediately, ensuring higher product quality and reducing waste.
- Maintenance Predictions: Machine learning models will predict equipment failures based on sensor data, allowing for preventive maintenance. This reduces unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery.
3. The Importance of Sustainability and MES in Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
As sustainability becomes a paramount concern in manufacturing, MES will play a crucial role in achieving eco-friendly production processes. Companies are increasingly focusing on reducing waste, energy consumption, and their carbon footprint.
- Resource Optimization: MES will help manufacturers optimize resource utilization, minimizing energy and material waste. Real-time monitoring of energy consumption and emissions will enable proactive measures to reduce the environmental impact.
- Circular Economy Practices: MES systems will support circular economy principles, where products and materials are reused, remanufactured, or recycled. Production planning will incorporate strategies for sustainable product design and end-of-life considerations.
- Environmental Reporting: MES will provide tools for tracking and reporting environmental performance. This data will be essential for compliance with sustainability regulations and for meeting corporate sustainability goals.
Manufacturers who embrace these trends will be better positioned to enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
Conclusion
MES has emerged as the backbone of modern manufacturing operations. Its ability to bridge the gap between the shop floor and the digital realm is crucial in achieving efficiency, quality, and agility. Through MES, manufacturers can streamline their production processes by automating tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing lead times. This not only enhances productivity but also improves customer satisfaction through on-time deliveries.
A culture of continuous improvement is promoted by MES, as it empowers manufacturers with data-driven insights to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and enhance product quality. By implementing MES in your organization, you empower your workforce to improve processes, and propel your business towards a future of greater efficiency and success.
Take a closer look at Hitechi2i – a powerful MES software
Interact with our product team and see how Hitechi2i’s powerful features can address your unique challenges.





